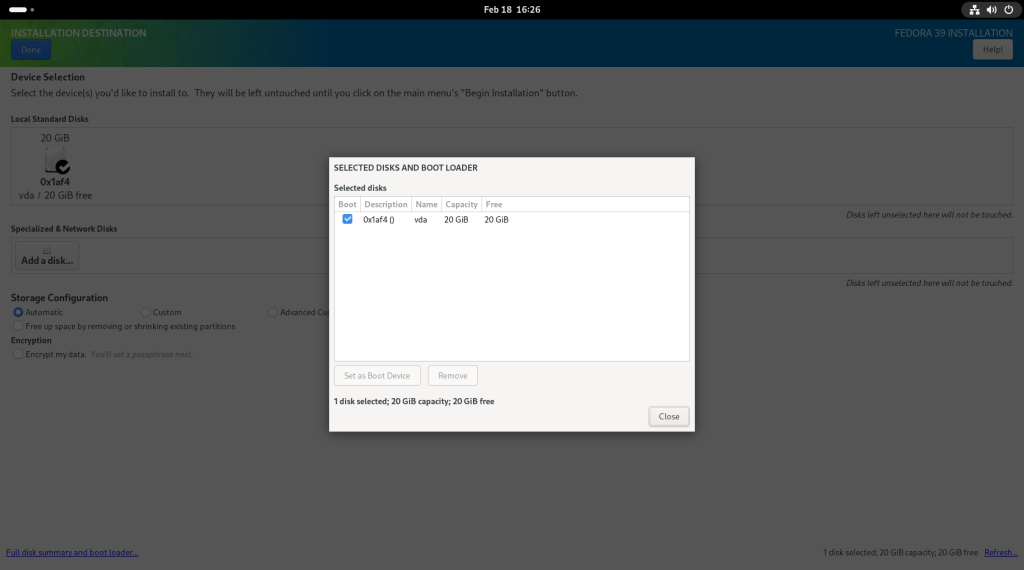
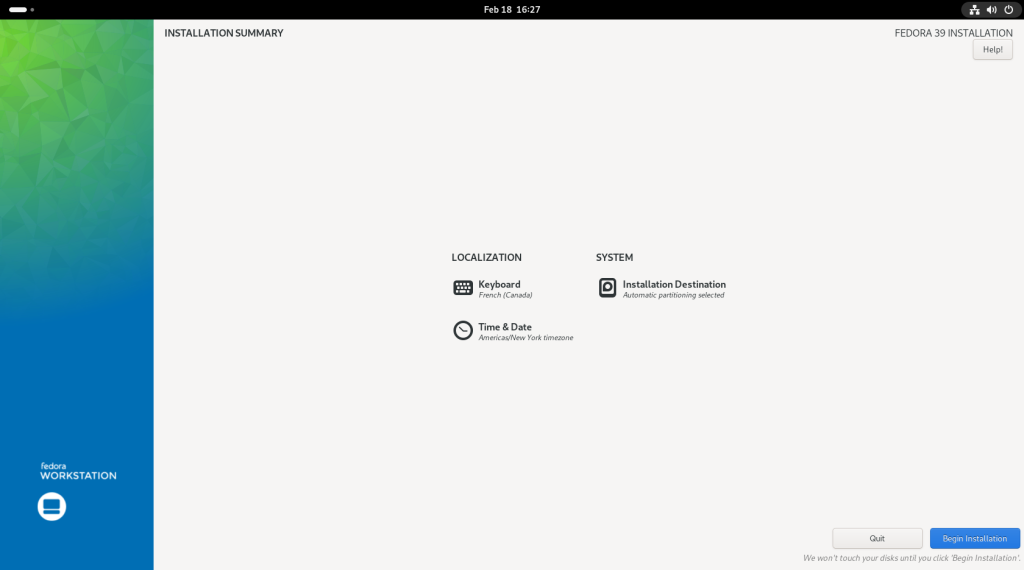
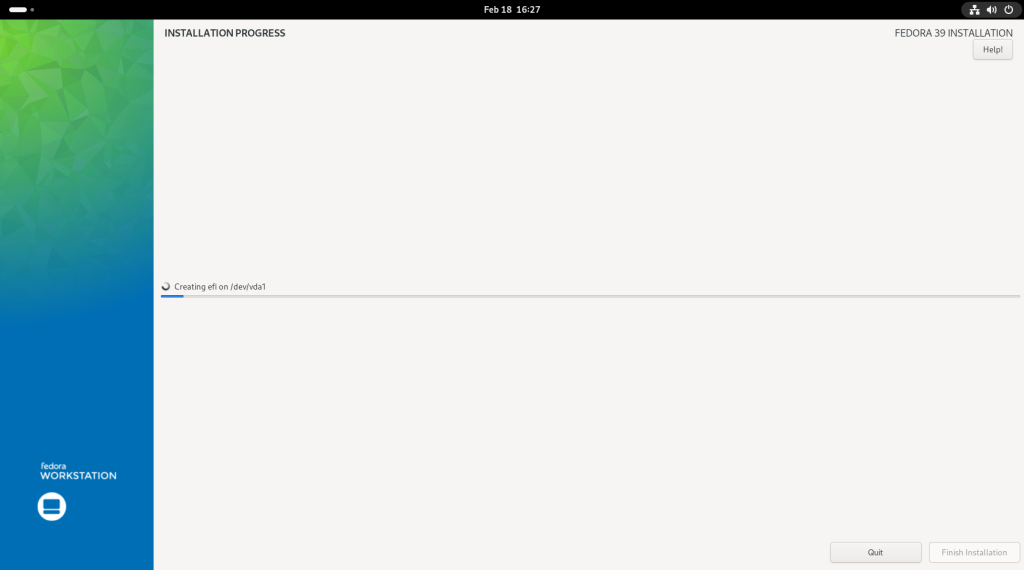
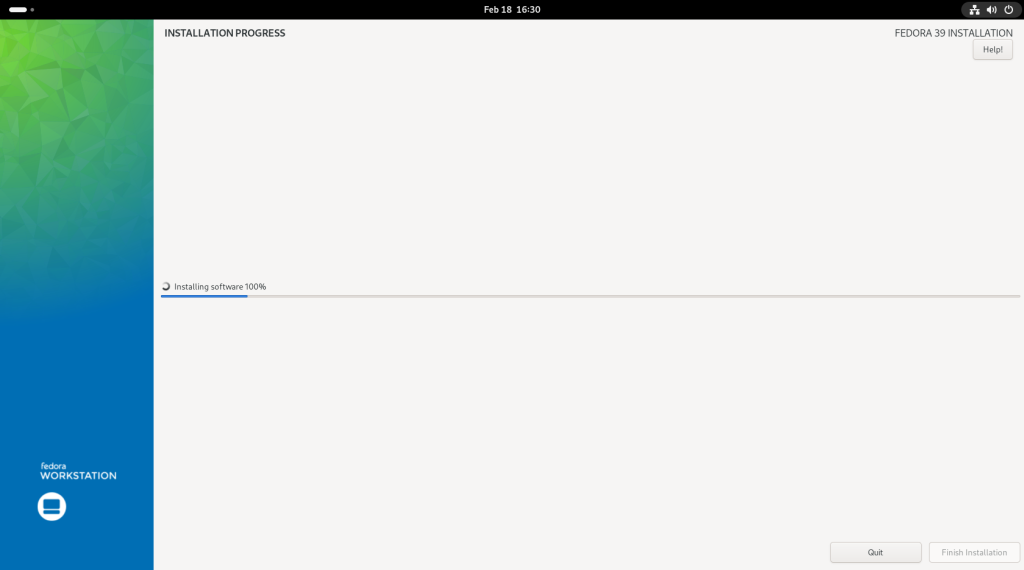
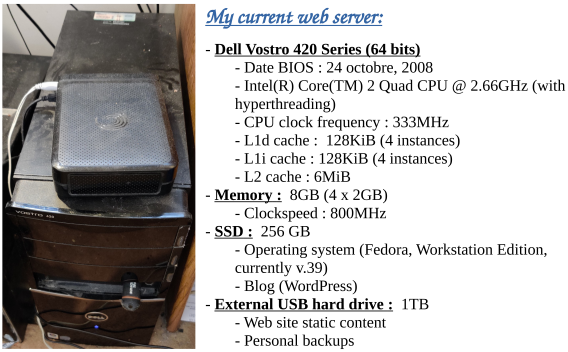
Previous chapter: Desktop Linux: Unveiled Chapter 6: Upgrading the Operating System
Using your computer of course requires some software beyond the base operating system; fortunately, most desktop linux distributions not only have repositories of freely installable software, often more common software as decided by the distro’s maintainers are pre-installed on the system at the same time as system installation.
This post is concentrating on the popular office suite LibreOffice which includes a drawing program, a word processor, a spreadsheet application, and a database application. While this post will show a few functions of each part, it is in no way intended to be a tutorial, but rather a cursory demonstration of each, leaving the exploration of each to you, the reader.
In this post I occasionally refer to operating systems beyond Linux. Also, contrary to my usual habit of not editorializing in this series, I offer the following: Many Linux software suites are largely, although importantly, not completely compatible with other known equivalents on other systems. They will often be able to open and edit files created by them; however, the compatibility and drop-in replacement value of each piece of software for the other (regardless of in which order) is often variable, sometimes quite substantially.
Note that occasionally, some screenshots were taken at different times for the sake of completeness, but presented in the order seen here, for the sake of the narrative.
Pinning Apps to the Dock:
Start from the Activities (hot corner in the upper left hand corner (the horizontal bar; either just quickly move the mouse there, or if necessary, click on the the horizontal bar):
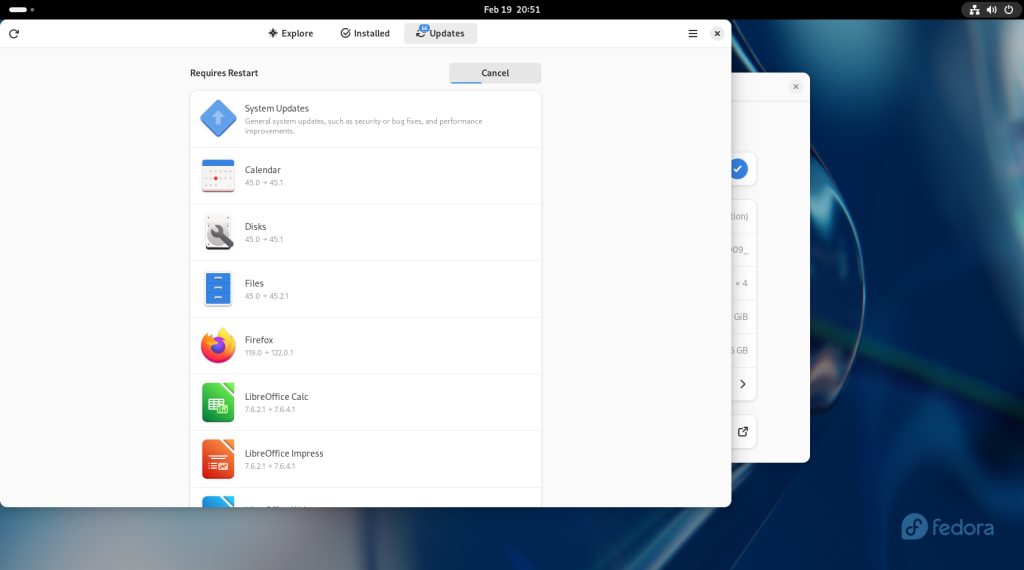
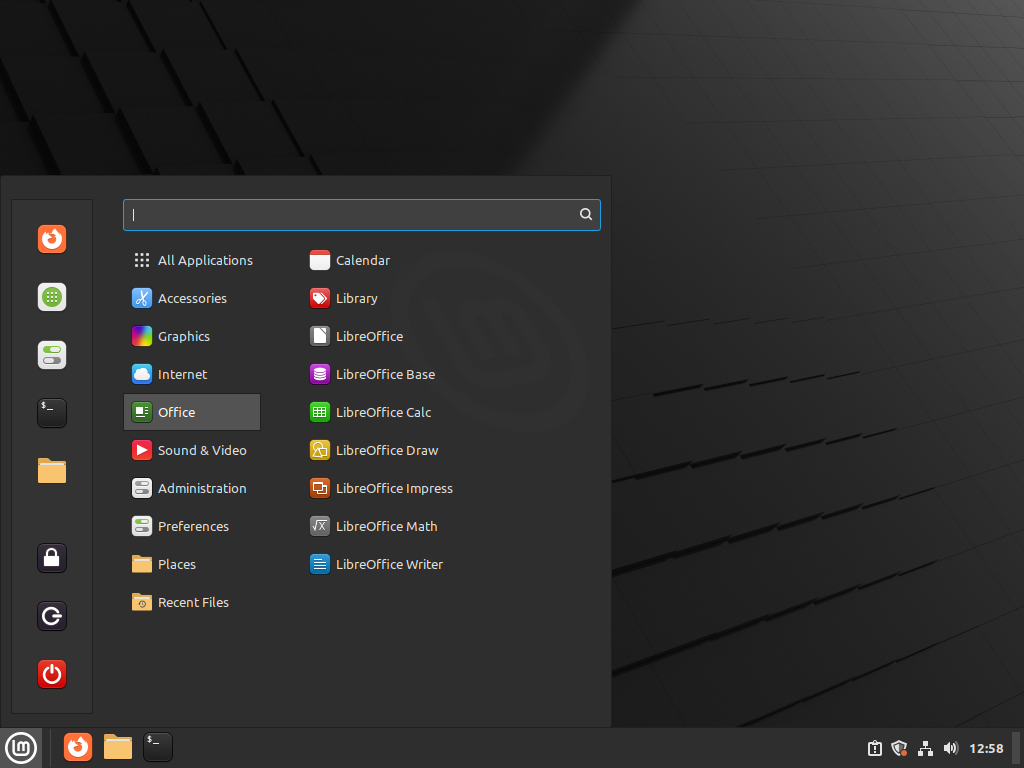
I searched for “Lib” which brought up three of LibreOffice’s apps: Writer, Calc, and Impress, and I right clicked each one …
… each of which I pinned to the dock at the bottom, one at a time:
Templates:
Note: In this post, the use of existing document templates found on the internet will be generously relied upon in order to demonstrate in a cursory fashion some of the resources available to desktop users — both of free software packages and other systems as well — as well as to simplify the mounting and development of the narrative using said existing documents. The site www.freedesktop.org, by happenstance, is frequently used, as is the templates section of www.libreoffice.org. Of note, especially on the former site, there are a number of templates which are in languages other than English, and some which have been on the site for several years, using older formats. Hopefully, the language barriers as the cases may be will not be too difficult to surmount given online translation services, while the older file formats are normally seamlessly supported by current software suites, with the ability to save in modern formats.
Users are of course free to create documents from scratch as they would on any system.
Going back to the activities screen, choose the Firefox icon (orange and blue, on the left at the bottom):
In the address bar, enter the address of a search engine, such as www.duckduckgo.com:
Search for templates. In this case, I specifically asked for templates appropriate for LibreOffice, which brought me to www.opendesktop.org:
In the search bar, I searched for LibreOffice, which gave me the following options:
… and chose for ODF Text Templates (for word processessing):
Browsing through the templates, I chose a CV template, for “Tux the Penguin — Brand Ambassador and Mascot”:
… which I downloaded:
On the activities screen, I opened up the Files application:
Drawing:
… and this is where I learned that the downloaded CV template was not what it seemed. 🙂
Much like other popular desktops, Fedora Linux has several fully functional and fully featured drawing software. One such piece is LibreOffice Draw, which functions similarly to Microsoft Visio, allowing for some basic-to-not-so basic graphical manipulations, editing, basic draughting, and inserting texts.
From the Files program just opened, I navigated to the Downloads directory, where the CV was located after downloading, and despite having believed that the CV I had downloaded was a text document, the file format in fact proved to be a drawing format:
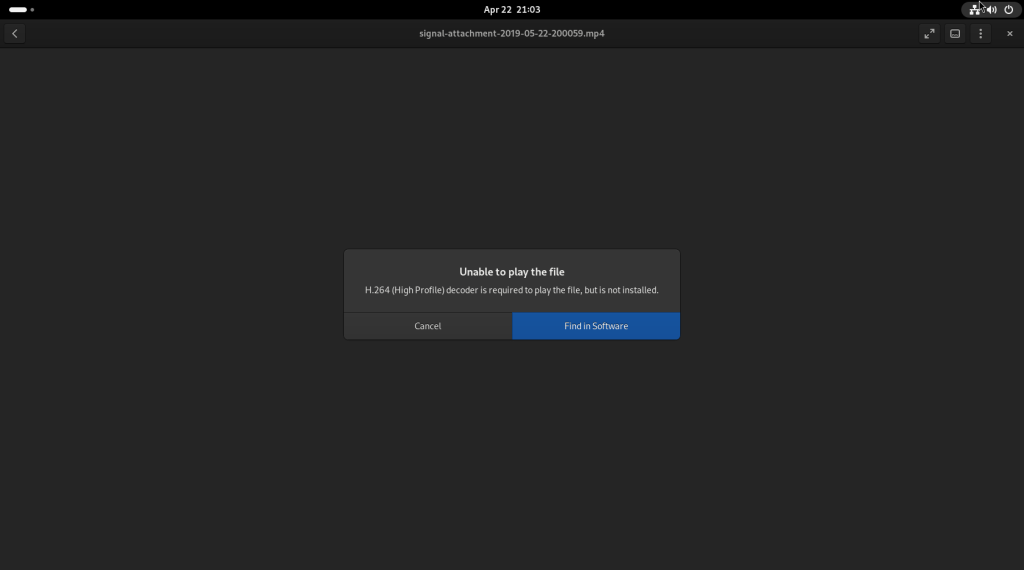
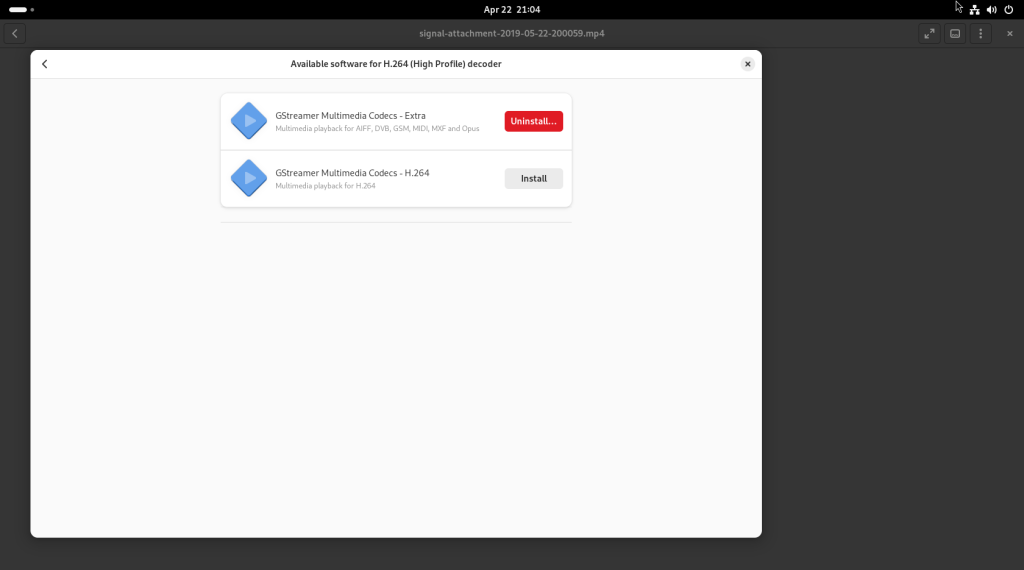
I double-clicked on the CV file, which, since LibreOffice Draw isn’t always a part of a Fedora base installation, launched the software store, and having found LibreOffice Draw in the Fedora repositories, offered to install it, which I accepted:
Once LibreOffice Draw had been installed, I asked that it be launched:
After closing the offer to see the “What’s New” notes, I went to the File dropdown menu to open the file:
… and navigated over to the Downloads directory, where the CV was located.
I clicked on the CV file to open it:
In Draw — depending on the nature of the input file — various existing texts can be modified, as well as many basic-to-not-so-basic graphical manipulations. In the case of this file, the file was designed such that the text could be modified:
To manipulate images, the picture of Tux (the penguin) was double-clicked to select it, the right mouse button was clicked, and the “Rotate or Flip” option was selected:
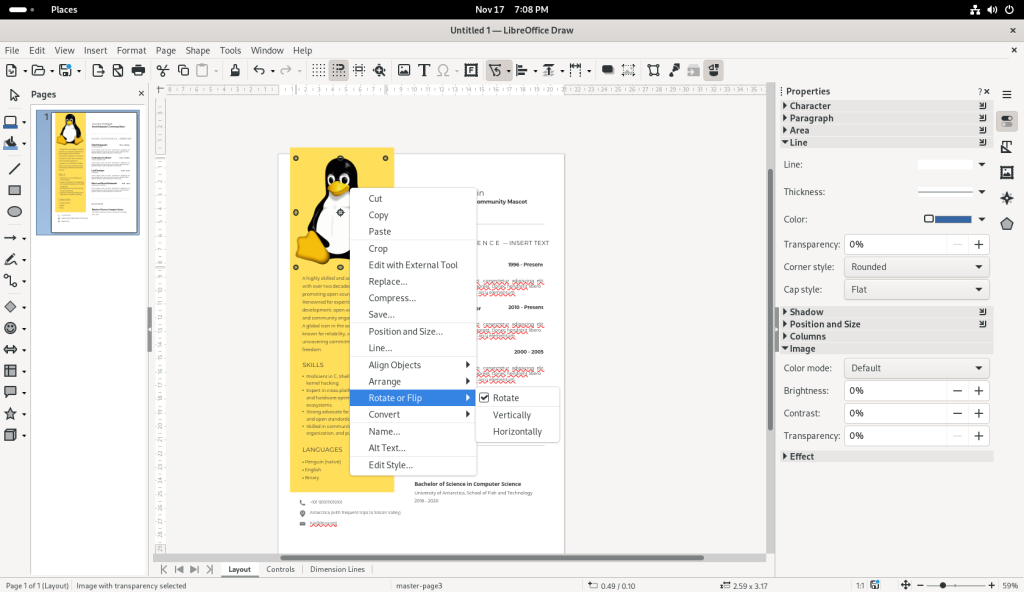
… and I chose to flip the picture of Tux upside-down:
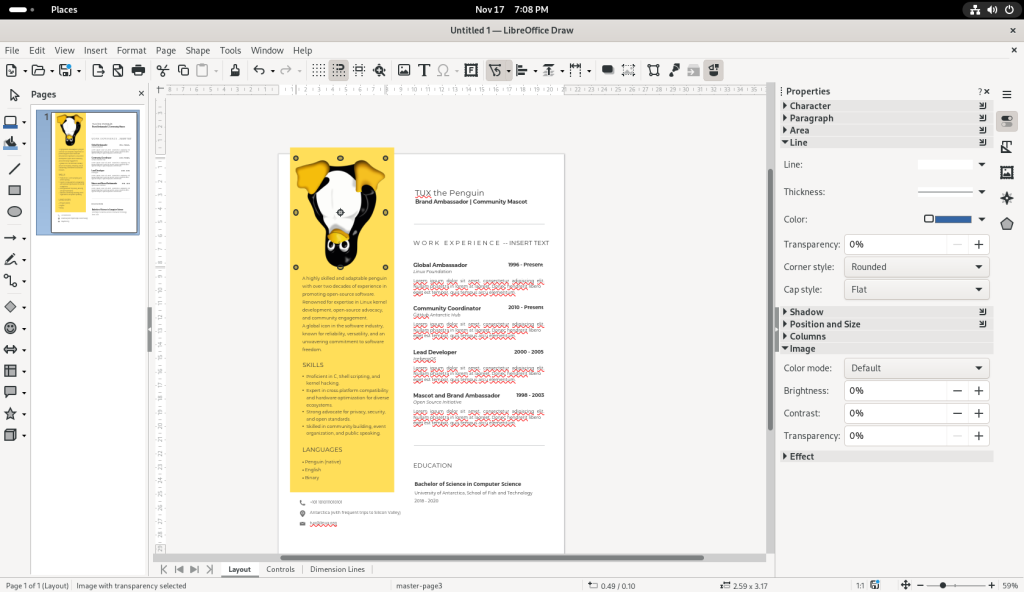
Some modestly — or more complex — drawings, including multimedia documents such as the CV shown above, can be created and / or modified, which I leave to the reader to explore.
Word Processor:
Much like other popular desktops, Fedora Linux has several fully functional and fully featured word processing software suites. One of the more popular such pieces is LibreOffice Writer.
I returned to the opendesktop.org website, and chose a business card template to open in a word processor — LibreOffice Writer.
I navigated to find a business card template:
… and downloaded the file:
Similar to how the CV above was opened, the business card template was opened, without having to go through the installation of LibreOffice Writer:
The text of the first card was changed to a “Desktop Linux: Revealed” theme:
The modifications were also saved:
Returning to the opendesktop.org templates, I chose the “Organica Business Forms” to download:
The page for the Organica Business Forms was opened:
… and the file downloaded:
The business forms were compressed in the .tar format, analogous to .zip files:
The archive was double-clicked, revealing a directory contained within:
The directory was double-clicked, revealing several templates: Business cards (different from above), a fax cover sheet, four different kinds and sizes of labels, an invoice, and a letter:
Going back to Writer, the letter file was double-clicked, which again opened the file in LibreOffice Writer:
A space was added between two paragraphs:
The “Table” drop down menu was opened:
… and the “Insert Table” option was chosen:
… which opened up a window to determine some settings for the table to be inserted:
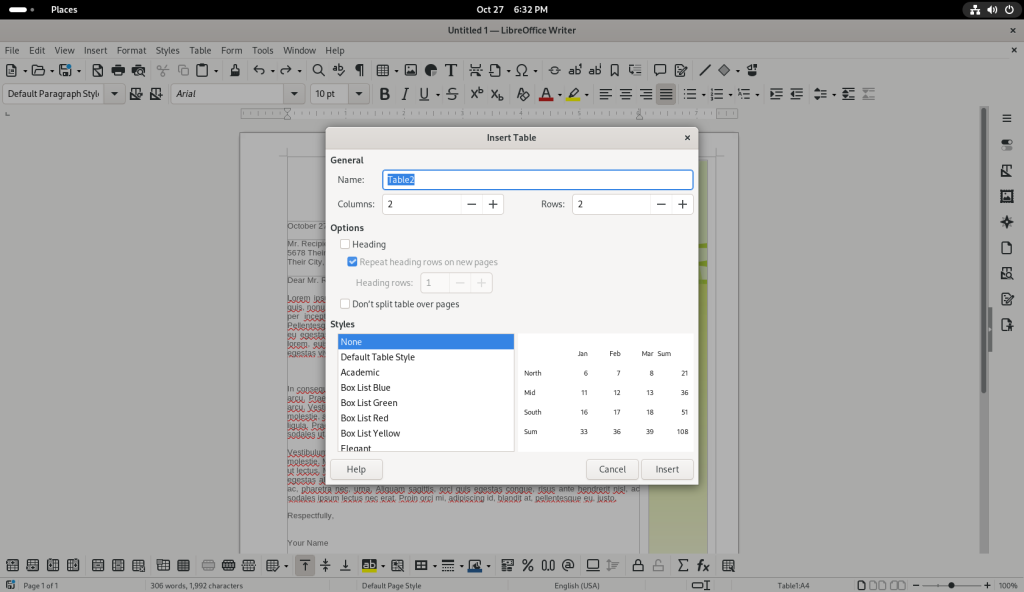
A table with five columns and five rows was selected:
The table was selected, and the right mouse button was clicked, revealing a contextual menu:
The option “Table Properties” was selected, bringing up a window:
The button for all lines under “Line Arrangement” was chosen in the Borders tab, in order to insert borders around all the cells of the table:
The “Ok” button was pressed, returning me to the document, showing now all the cells of the table with borders:
Text was added to a cell in the upper left hand corner (“Linux Desktop”):
A number of other cells were filled in:
The “File” drop down menu was opened:
… and the file was saved:
As with the previous section, I leave it to the reader to further explore LibreOffice Writer to see the various options in the various menus, and the various kinds of text documents that can be created.
Spreadsheets:
Much like other popular desktops, Fedora Linux has several fully functional and fully featured spreadsheet software. One of the most popular such pieces is LibreOffice Calc.
After saving the business cards, I returned to the freedesktop.org website, browsing the spreadsheet templates:
I chose the Amortization Schedule:
The amortization Schedule was downloaded:
Similarly to previous files, the Amortization Schedule was opened (file double clicked in the file download directory).
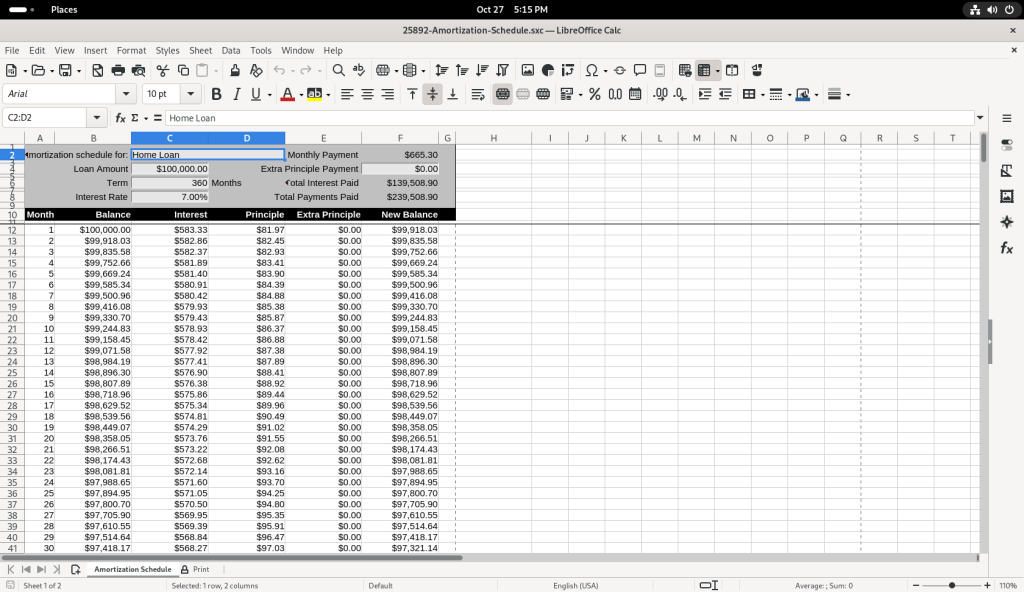
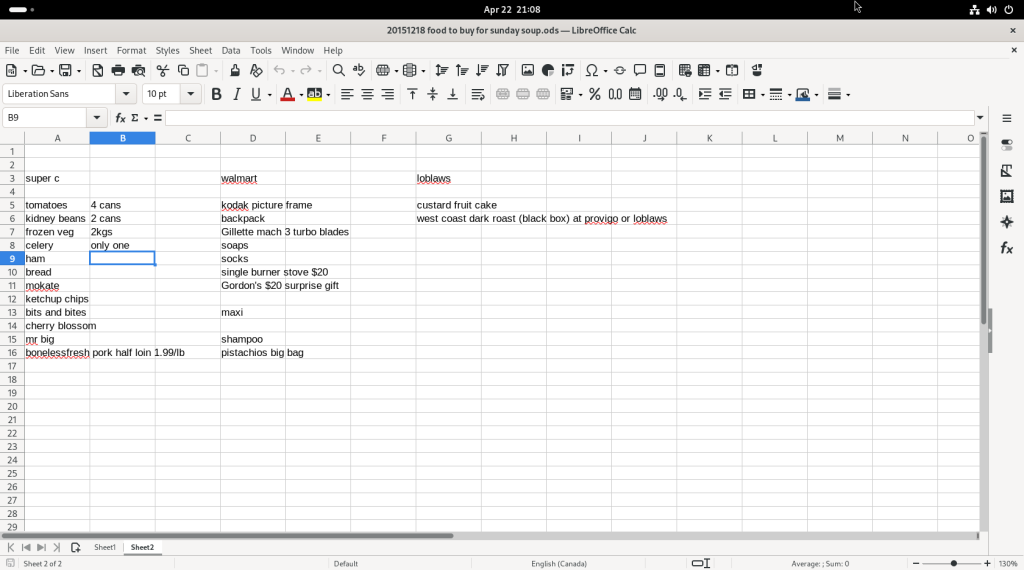
Several of the balance figures was selected, revealing how the value us calculated in the formula bar:
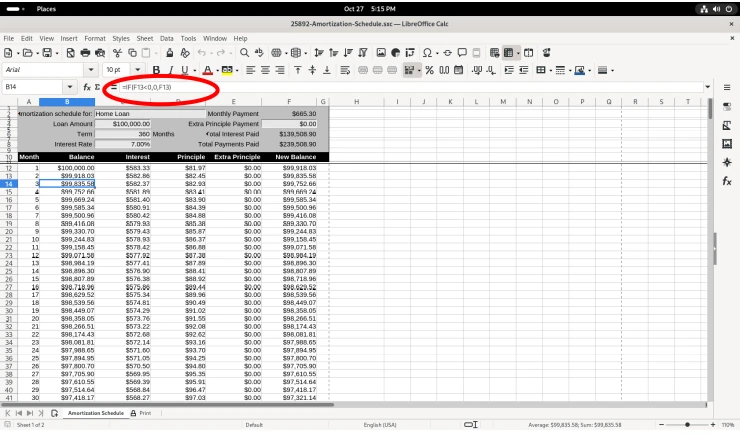
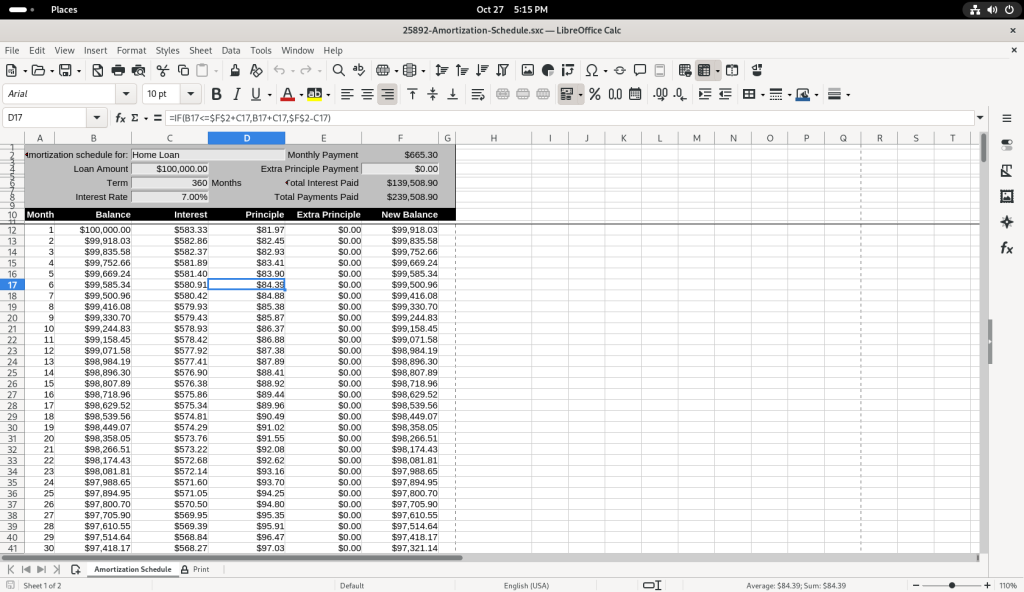
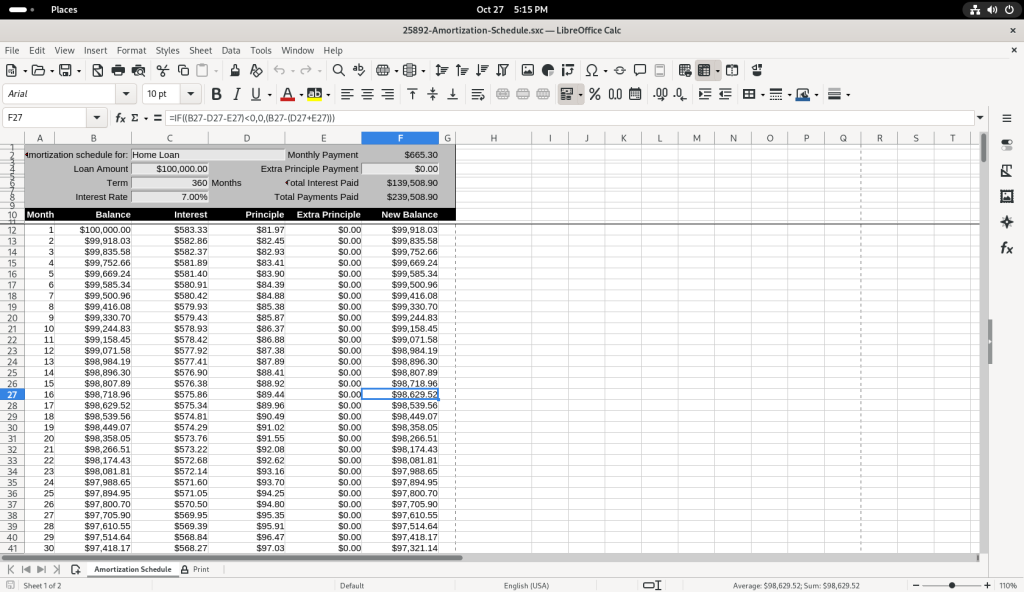
I chose to modify the table, by adding a value of 1000 in the “Extra Principle Payment”, to change the values of “New Balance” …
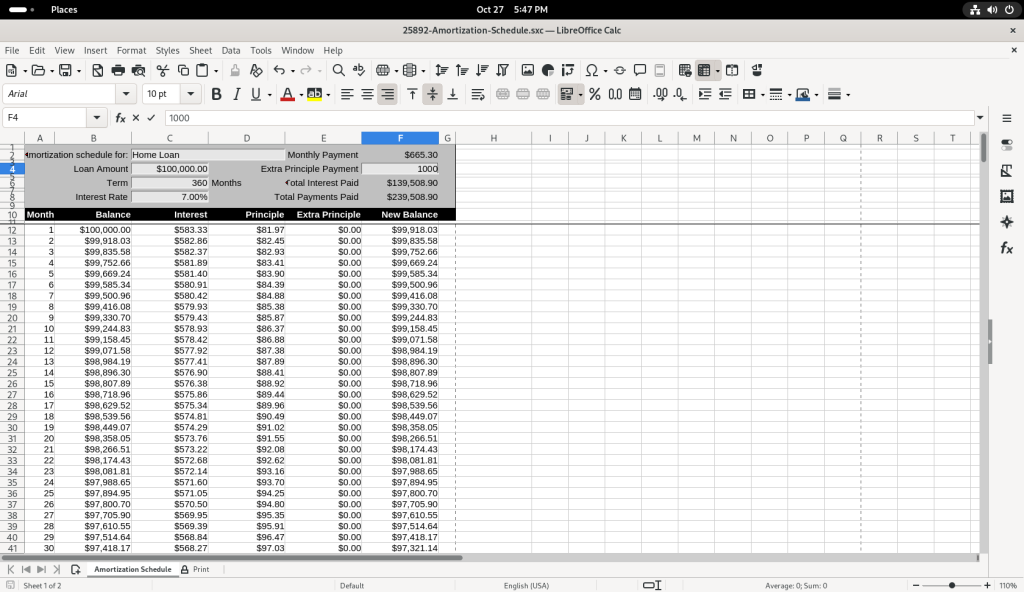
… and then I changed the value to 500 to see how it affected the values of “New Balance”.
Again I leave it to the reader to further explore mounting spreadsheets of their own using their own data.
Slide Shows / Presentations
At the opendesktop.org collection of templates, I chose a slide show template to download:
I chose a template to download …
… and downloaded it:
Again through the files directory, I double-clicked on the downloaded file:
… which opened up the file in LibreOffice Impress:
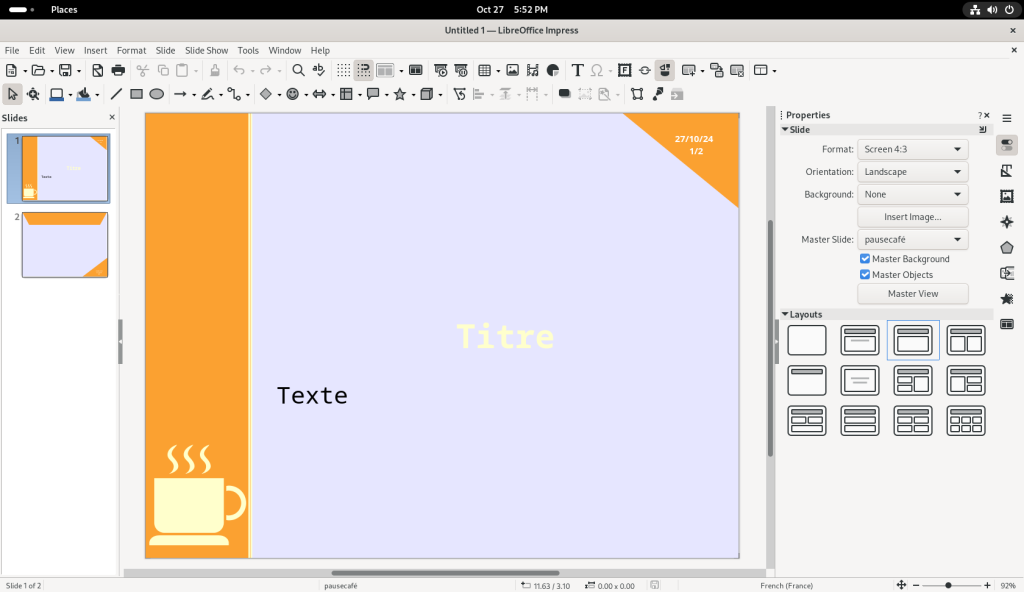
I began editing the title line — in the process, using the wrong branding for this series!
The text colour, white, didn’t have enough contrast for my taste, so I selected the text …
… and went into the options area on the right to by clicking on the letter “A” with a red underline, to change the font colour:
The font colour was changed to a greenish-blue colour:
 Text colour changed to a greenish-blue
Text colour changed to a greenish-blueOther text was changed and added:
I changed to the second page, and similarly started to change the text:
Text can be changed as per your needs, as well as pages added through copy / paste or other wizards available.
The drop-down file menu was chosen, so that I could save the file:
Once the file was saved, I opened up the drop-down file menu again, and chose “Export As” so that I could export the file as a PDF. (Editorial note: As mentioned earlier, while there is a good amount of compatibility between LibreOffice and other office suites, it can be disappointingly incomplete, which I have particularly seen and experienced with — but not only — slide shows. For more of a discussion of such from the perspective of the usefulness of PDFs, please see my post on the subject.)
The file drop-down menu was clicked again, and the option “Export As” was clicked:
Exporting to PDFs can be rather easy and direct, or, as I am going to show a little bit here, allows for a large amount of choices …
… including protecting PDFs with passwords for opening:
Passwords were set for both opening as well as for “permission” which means to allow editing of the PDF (see my post on the subject), and the slide show was exported as a PDF:
… and the OK button was clicked:
As usual, I leave to the reader to explore further. Also, within LibreOffice itself it has a wizard to help the user create a number of presentations with various backgrounds and layouts.
Database:
LibreOffice also includes a database module, called “Base”, which is similar to Microsoft Access; it is essentially a front end manager — a gui interface — for the actual database software behind it that it leverages.
Before I show a properly mounted database, I will show some screenshots about how to start.
Starting from the home screen, the activities corner (hot corner) in the upper left was clicked:

On the Activies screen, “libreoffice base” was typed into the search bar, and the option to install LibreOffice Base, which is not always installed in a base install, was offered:
The option was double-clicked, which brought up the “software store” with the choice of LibreOffice Base …
I double-clicked on the option, bringing up the information page on the package and the offer to install it:
I clicked the “Install” button:
Once LibreOffice Base was installed, an “Open” button presented itself:
The “Open” button was clicked, lauching LibreOffice:
A wizard came up to select a database:
The presented option was accepted, and the “Next>” button was clicked, bringing up a “Save and proceed” window:
The “Finish” button was clicked, opening a Save window:
Once that was done, the following screen came up, in order to start creating a database:
Note that from this point on, I am showing some very basic things, and I will soon recommend a tutorial, which will better show how to use the software than I could ever present.
I clicked on the “Table” icon, which brought up a Table Wizard:
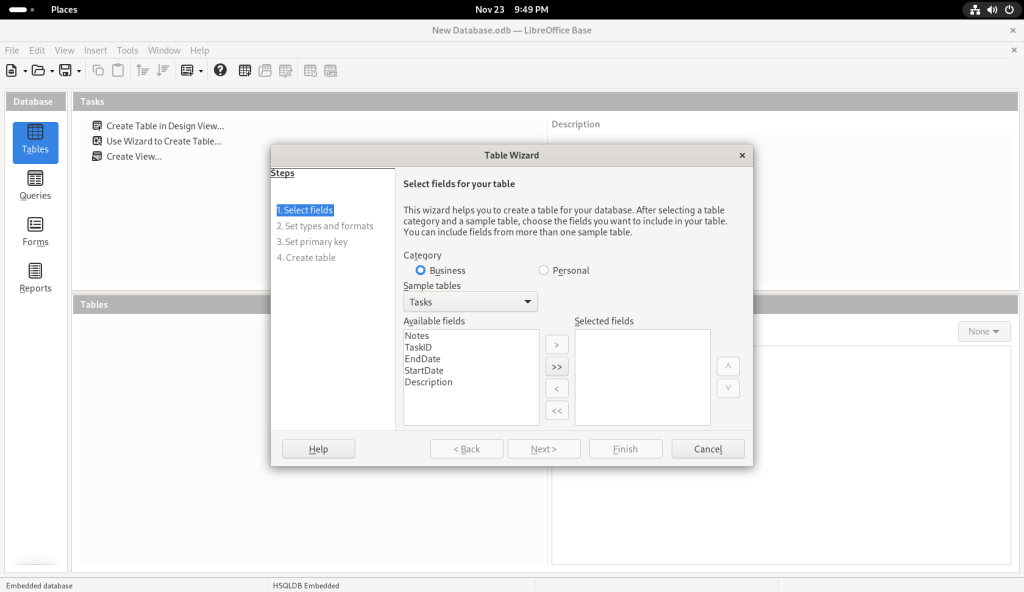
I chose the “Personal” category, on the premise — in the context of this post, anyway which presumes that many readers may be seeking to use linux at home and not just at the office, and that a database might not as easily appear to be a personal piece of software.
I pulled down the suggested list of topics:
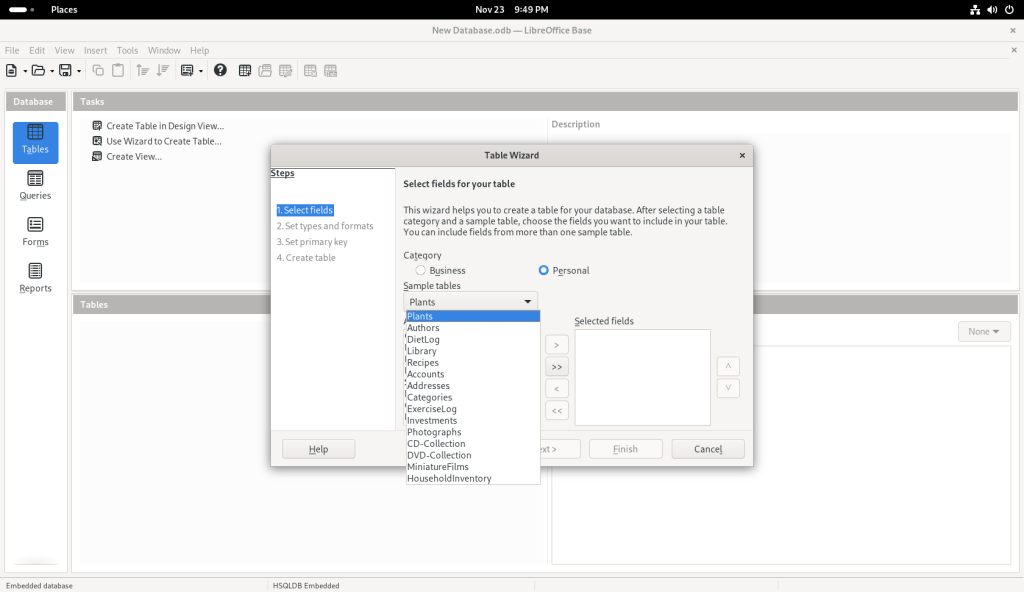
… and chose “Recipes” for what I presume are obvious reasons — we all eat, and presumably many people have a personal collection of varying sizes (here’s my collection of recipes, incidentally NOT in a database format, at https://www.malak.ca/food).
Some field names were suggested:
I clicked on “Name”:
… which moved it over to the column on the right:
I also chose other sample tables:
… at which point, I clicked on the “Finish” button, leading to the following screen:
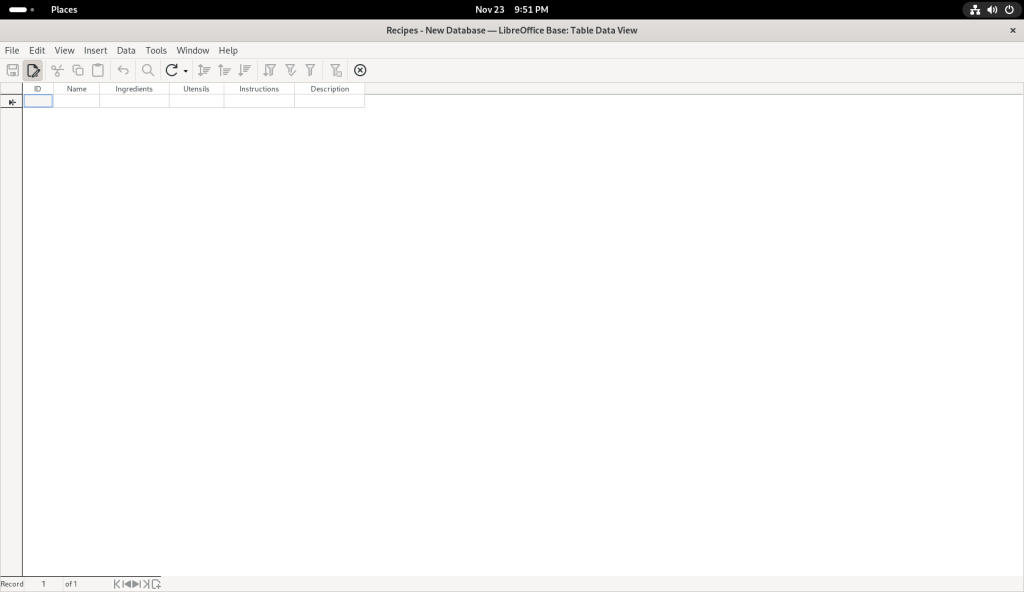
I started entering data:
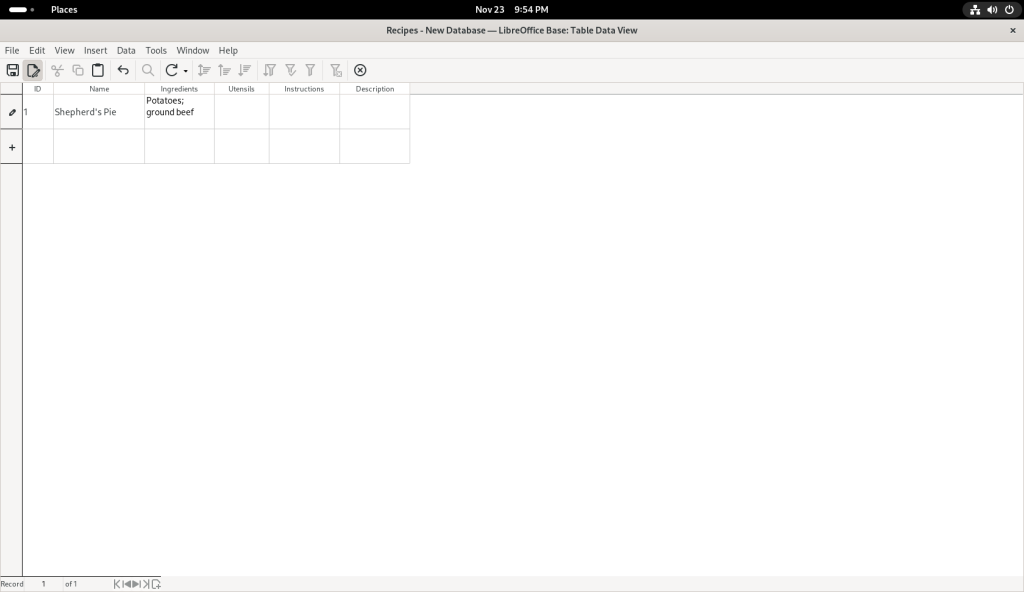
I chose to save my changes:
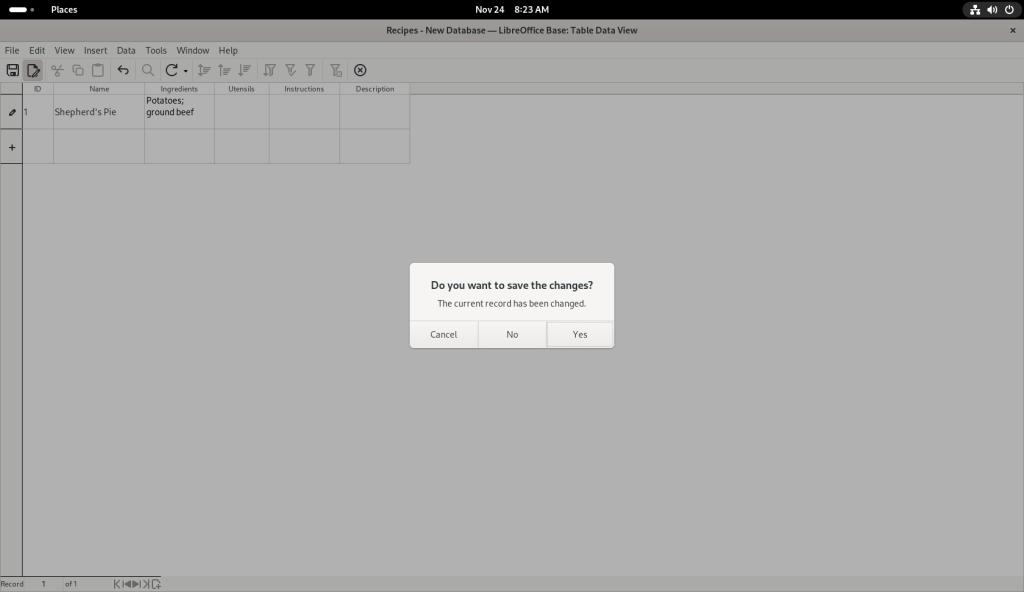
At this point, I am going to direct you to a far better tutorial than I could ever present, even in the most cursory of fashions:
As of the writing of this post, a rather complete tutorial on using Base can be found at thefrugalcomputerguy.com/seriespg.php?ser=15/ (no doubt amongst countless other similarly excellent resources):
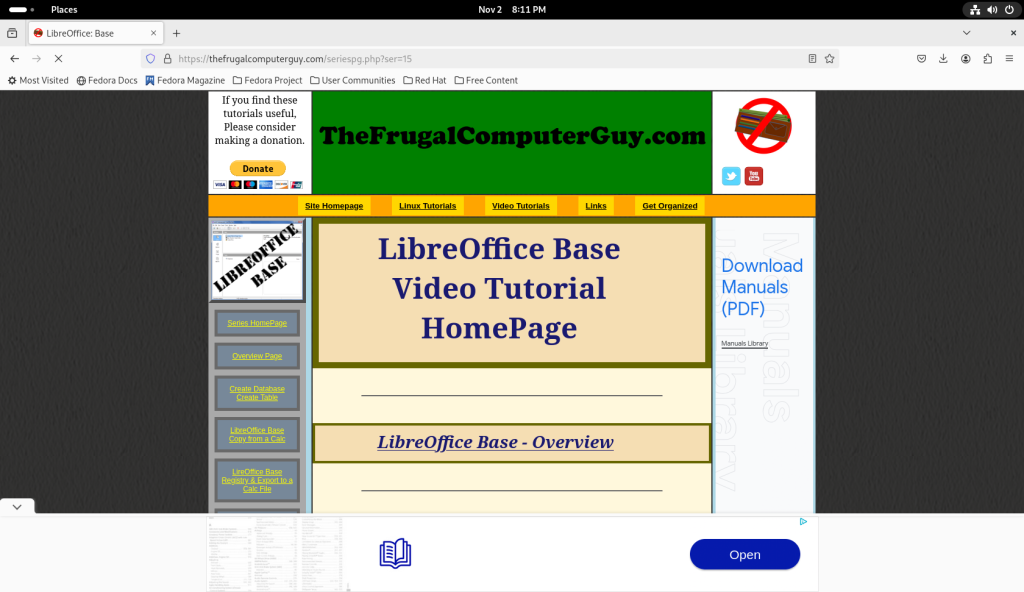
Although I think it best to leave the tutorial to TheFrugalComputerGuy, I will show a small database in action:
Starting again at the desktop screen:

The activities screen was accessed through the upper left hand hot corner with the mouse:
The Firefox icon (orange, on the left on the dock at the bottom) was clicked:
I went to my favourite search engine, duckduckgo.com:
… and I searched for “libreoffice base templates”:
I chose the “Templates & Extensions” link, the second link above, at the LibreOffice.org site itself:
I clicked on the green “plus” sign to the right of “Boost your creativity with templates”:
… which led to the following page:
On the left, there are a number of filters under “Add tag filters:”, and clicked on “Base”, bringing up the following page:
I chose the “MyRecipes” template for LibreOffice Base:
I scrolled down to quickly assess the files, finding them eminently interesting for the task at hand:
The download button was clicked, and the file downloaded:
The files program was opened, and the newly downloaded file was highlighted:
The .zip file was double-clicked, creating a directory of the files (ok I accidentally created the directory three times!)
One of the directories was double-clicked and opened:
The “ReadMe.txt” file was double-clicked and opened:
The .odt file was opened as well:
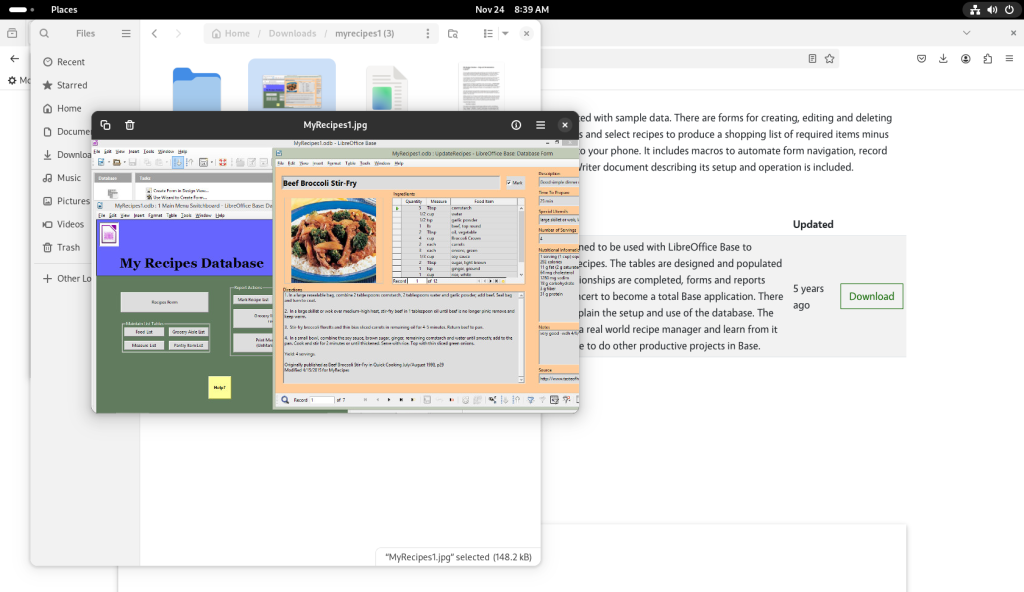
The “MyRecipes1.jpg” file was double-clicked, opening a screenshot:
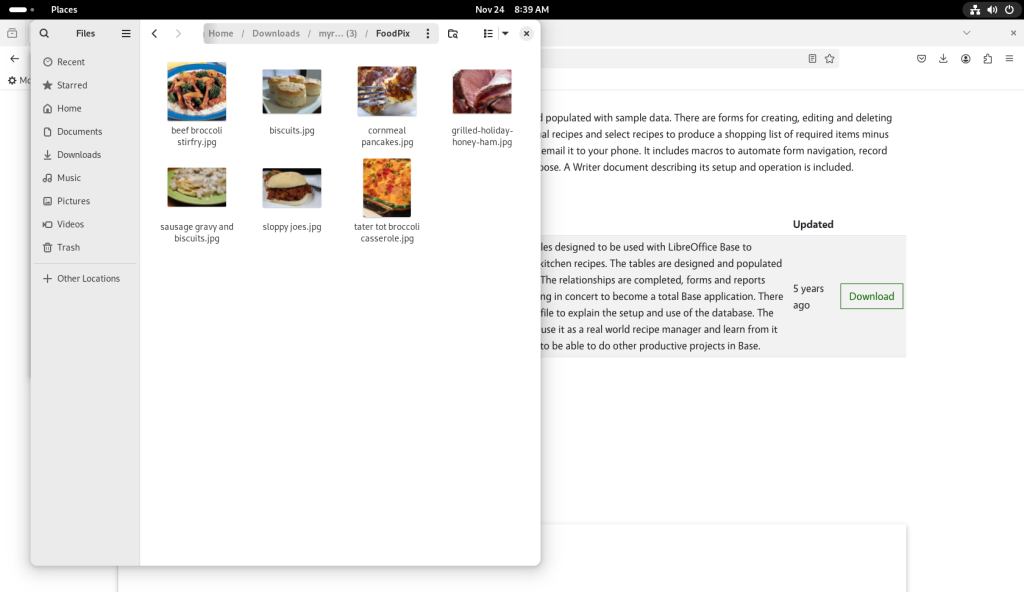
The FoodPix directory was opened, showing pictures of the recipes in the database:
From the database’s main directory, the database was opened:
After looking about, the “UpdateRecipes” option was selected:
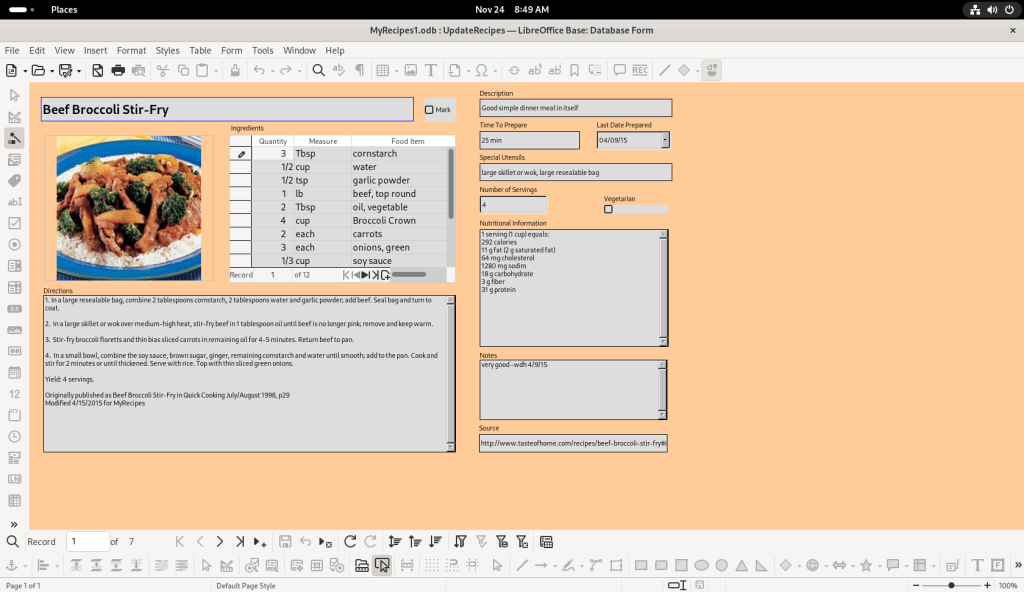
Which opened up one of the recipes:
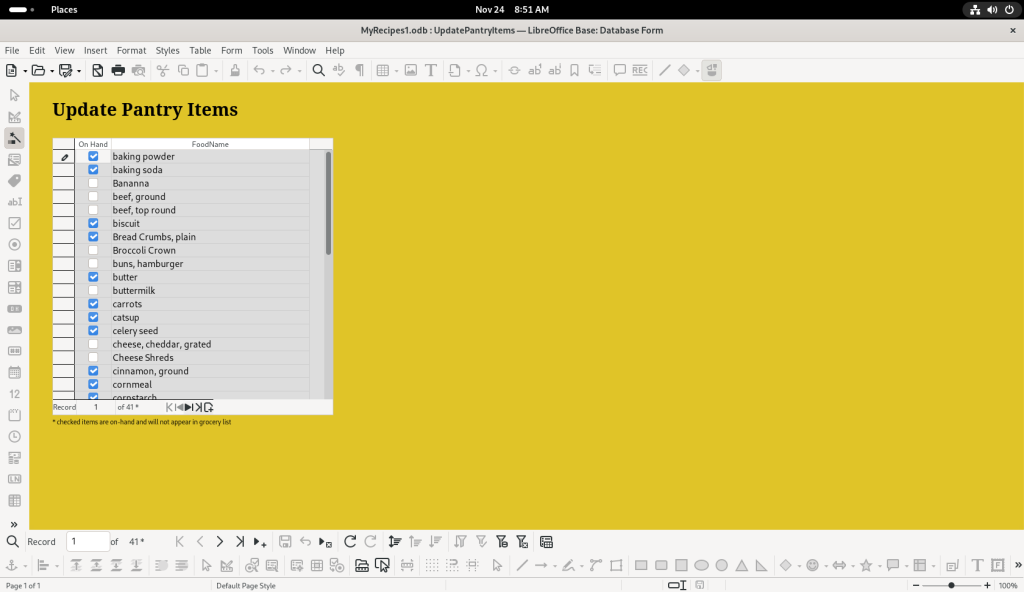
The database author chose to have an active Pantry list with checkable items, no doubt based at least partly on their recipes; by having it dynamic, when asked to create purchasing lists, the database can exclude pantry items already on hand:
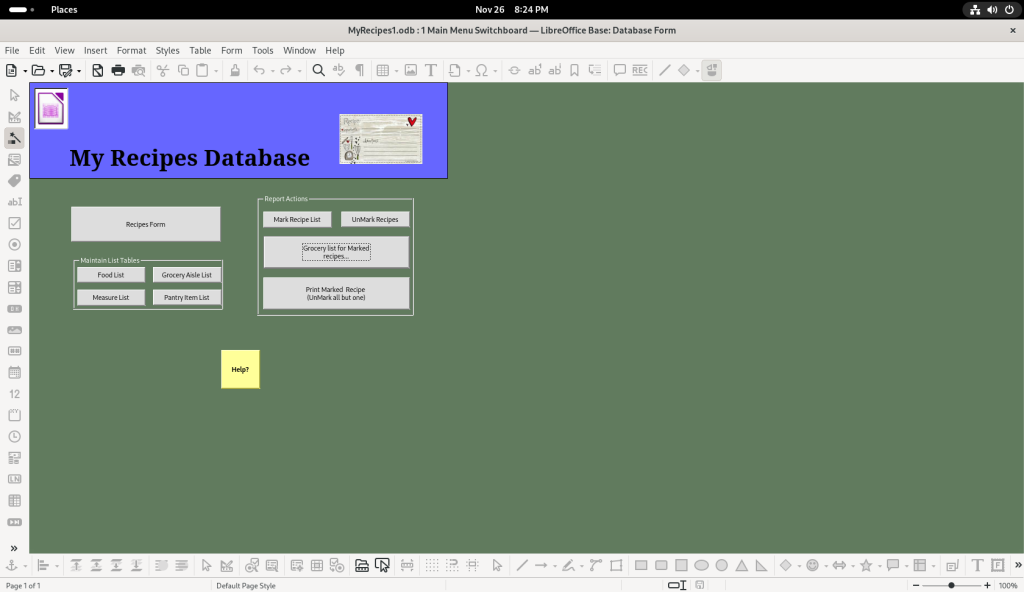
Said shopping lists can be generated from the “1MainMenuSwitchboard” option:
Given that the “switchboard” is based on macros, the Tools pull down menu was opened::
… and the “Options” option was clicked:
The Security option was chosen:
… and the “Macro Security” button was clicked. The security level was set to low, as per the author’s suggestion:
Back to the Switchboard:
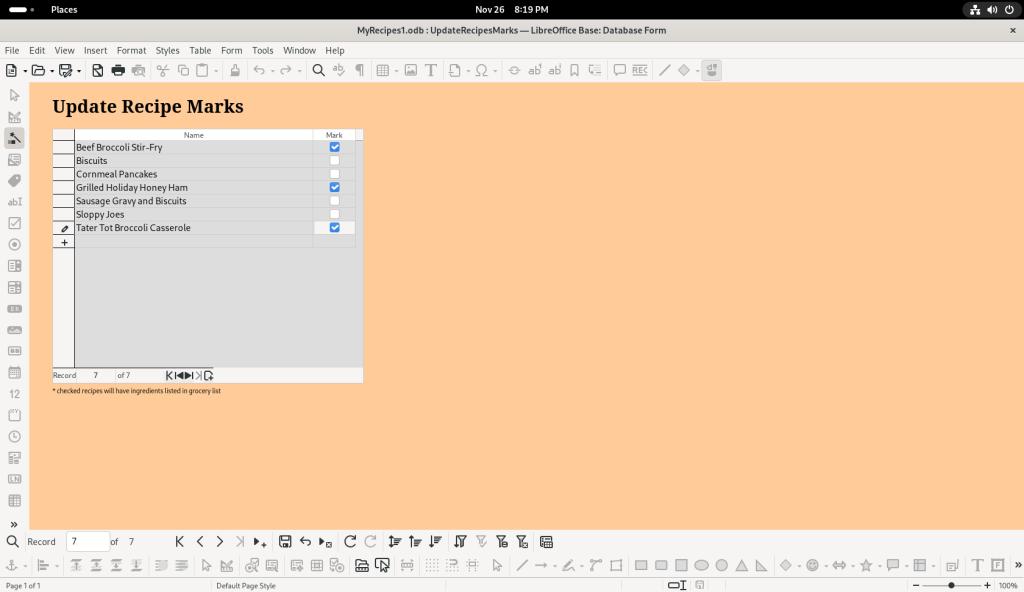
The “Mark Recipe List” button was clicked, and I decided to mark three of the recipes:
In trying to close the window, a window asked if I wanted to save my changes, to which I clicked “yes”.
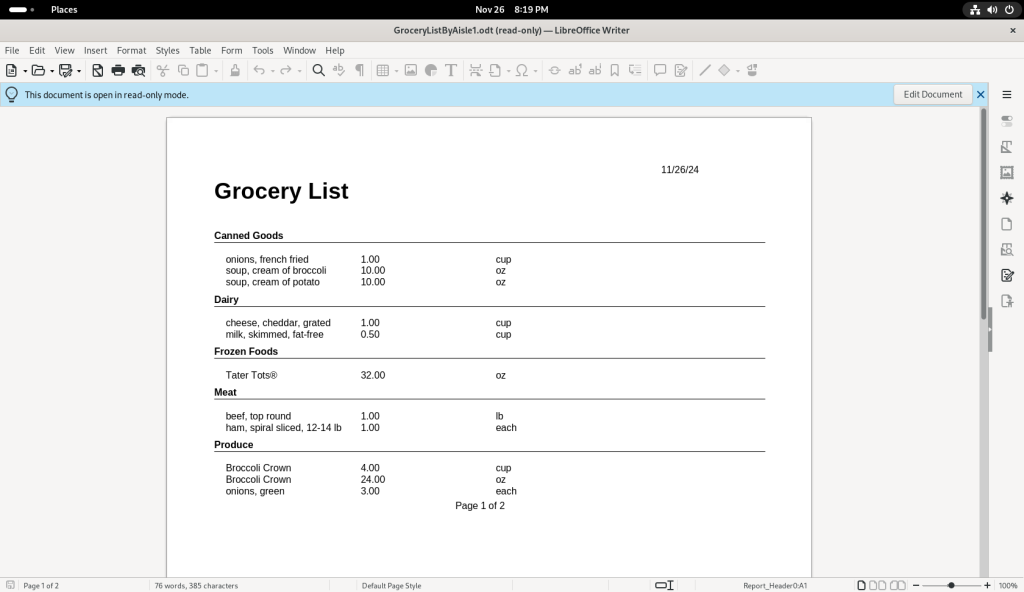
The “Grocery List for Marked Recipes” button was clicked:
… producing a grocery list based on the recipes, which was automatically opened in LibreOffice Writer:
The next chapter will look at graphics.