This post is a translation of and (somewhat of an) adaptation, as well as slight update, of a presentation I gave in November, 2021, at a meeting of my local Linux Meetup. This adaptation includes some extra limited mockups of demonstrations performed live during the presentation.
The presentation was put together using Fedora Workstation (a general purpose version of Linux, in this case specializing in being a desktop workstation), highlighting some software either installed by default, or available in the Fedora Linux and rpmfusion software repositories (“App Stores”). It is therefore not intended to be a complete exposé on all available open source / free software options for PDF, even under Fedora Linux, let alone GNU / Linux in general, or other systems.
It should be noted that the presentation’s original target audience was a French-speaking group of Linux enthusiasts, Linux professionals, and other IT enthusiasts and professionals familiar with Linux. Most of the listed software would typically be available in standard or easily accessible Linux software repositories (“App Stores”). Beyond the world of GNU / Linux, free software is generally available for use on other systems, and, barring instances of a specific given package offered with paid warranty support, are usually also free of charge to download, install, and use.
In the case of the software highlighted in this post, all are either free-of-charge, or represent the free-of-charge version.
The Value of a PDF File
Context / Situation:
Take the case of the exchange of a document between two computers — such as between one running Linux, and another running Windows (or vice-versa) — and each computer is endowed with a different office suite, such as LibreOffice (cross-platform) on one, and Microsoft Office (Windows / Mac) on the other. (Of course, other possibilities exist, such as Calligra Suite (cross-platform), Pages / Numbers / Keynote / etc. (Mac), Corel Wordperfect, Google Docs, etc.)
LibreOffice, and in days gone by, OpenOffice.org, have long been touted as being “compatible” with MS Office; this purported compatibility, however, is disappointingly nowhere near as good as I and many others would like to believe.
As such, each user will open the shared document, which will be displayed according to each suite’s interpretation of the file, and may find that the actual displayed content on their screen could be different — sometimes substantially so — from the intended original display of the document. Text lines may be cut off; fonts may not be available on one or more of the systems, causing font substitution; font sizes may be changed, or text size may be different while substituting a different font due to the lack of the specified font; certain symbols may not be available on some systems; table effects may not work, or objects inserted into tables may not function or be displayed as expected, such as the insertion of a spreadsheet.
Unfortunately, I would estimate that said disappointing lack of “complete and perfect” “drop-in replacement” compatibility is a very common experience in comparing many well-known pieces of proprietary software and their open-source counterparts — not just LibreOffice and MS Office. Personally, as a Linux user, I have experienced this lack of complete compatibility a number of times since beginning to use OpenOffice.org in 2005 and Linux in 2006. Since then, I have also seen the incompatibility in action on a number of occasions during varying presentations under completely unrelated circumstances in which the presentation files were produced in one suite, and attempts made to show them in another were met with varying degrees of disappointment, sometimes leading to complete failure.
Example PDF
The PDF at this link is a somewhat varied although basic document created for this presentation (you will need a PDF viewer); images of the PDF are shown below. It was developed in order to use throughout the presentation as an example PDF to demonstrate the various given points at hand. It should be noted that the PDF was written in French because the presentation’s original target audience was French-speaking.
The following four images are jpeg images of the pages of the PDF document linked to above, and which I created in LibreOffice Presentation. It should be noted that, for the sake of argument, the pages could have been created in another format, such as a word processor, a spreadsheet program, or a drawing program, for instance.
Page 1 — Song lyrics to be displayed for a Karaoke Night

Page 2 — Expenses list for a Luncheon

Page 3 — TV Listings
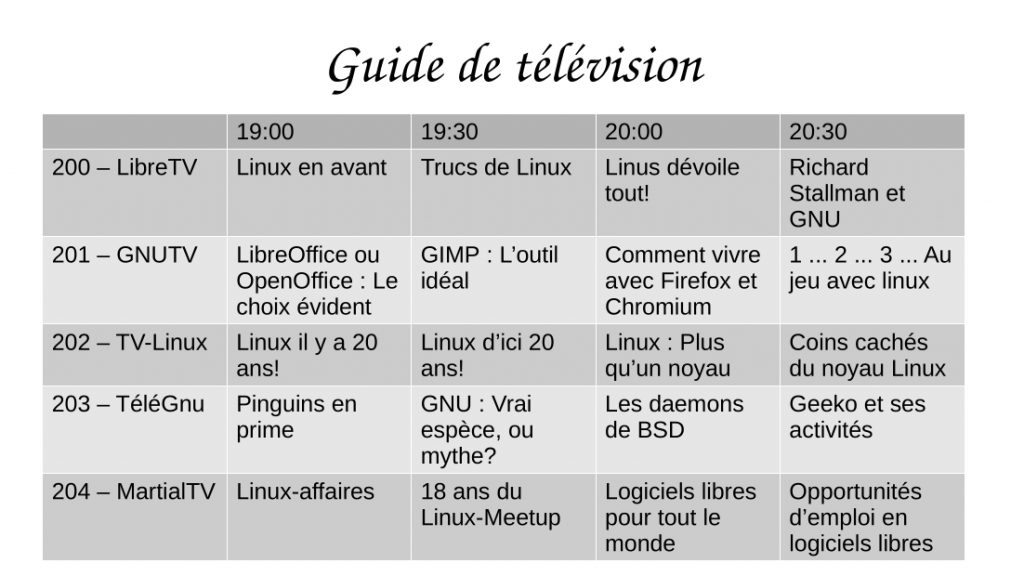
Page 4 — Flea Market Poster

The above document — represented here in jpeg format directly produced from a PDF of the document — was originally prepared in LibreOffice Presentation, and therefore correctly represented the original document.
However, the following four images are jpeg images of the pages of the PDF document I created in Microsoft PowerPoint (you will need a PDF viewer) into which I imported the original LibreOffice Presentation, in order to demonstrate the relative lack of compatibility between, at least in this case, LibreOffice Presentation and Microsoft Powerpoint.
Page 1 — Song lyrics to be displayed for a Karaoke Night
Changes: Text fonts and font sizes, causing text to be cut off the page

Page 2 — Expenses list for a Luncheon
Changes: Text fonts, and improper translation of symbols

Page 3 — TV Listings
Changes: text fonts, font sizes, and lack of background colours in the various cells
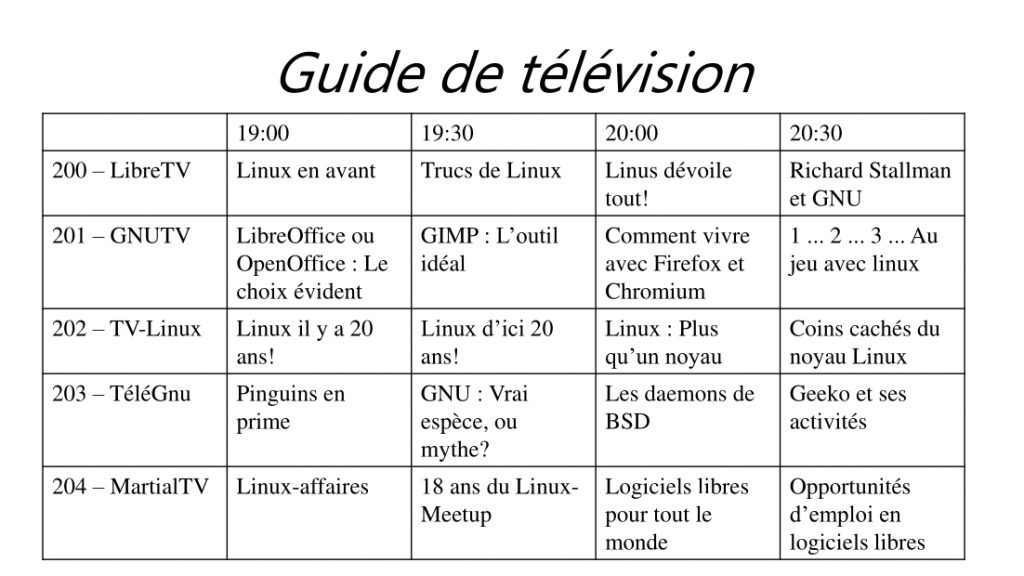
Page 4 — Flea Market Poster
Changes: Text fonts, font sizes, corrupted translation of spreadsheet table in the centre of the flyer

The value of a PDF:
PDF files are generally well supported across multiple platforms and software, generally regardless of platform, and will usually be displayed in a virtually identical fashion on all systems; in the case of discrepancies, they are usually inconsequential.
However:
There exists a certain perception that, short of having Adobe Acrobat Pro (a commercial, closed source piece software), PDF files are difficult to edit and modify, allowing for a certain view that PDF files are more secure. This is a case of “security by obscurity”, since editing and modification may be performed by many pieces of software, besides but of course including Adobe Acrobat Pro.
PDF files may also benefit from a perception of being less susceptible to viruses and malware, such as through macros. Suspicious files, regardless of format, should always be checked when there is reasonable doubt, particularly under certain environments.
Warning:
Be careful when using some PDF software downloaded from random websites on the internet, or websites which advertise PDF modification: The may add watermarks to the resulting file — this may be undesirable, and embarrassing, particularly if the software, website, or their output aren’t vetted prior to distributing the resulting file.
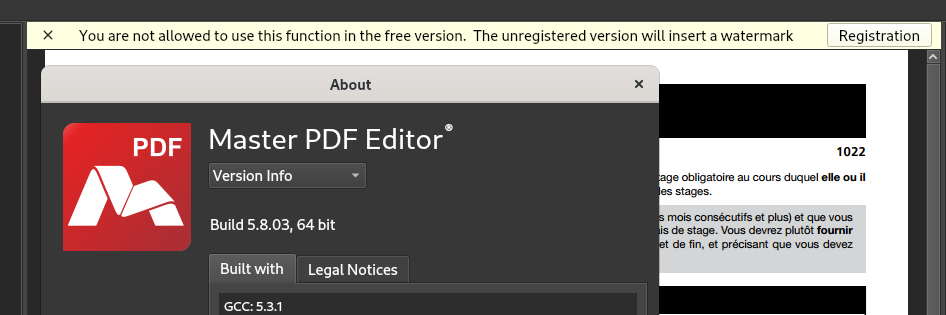
Further, websites providing PDF editing services may have very reasonable terms of service for editing your document, limiting their responsibilities toward you. By submitting a document to an external website, it may may not be able to protect personal privacy, nor be able to guarantee to not divulge commercial or industrial secrets or confidential personal information contained in the submitted document: They may become the victim of a hacking, or become the target of legal proceedings, not to mention potential dubious or unscrupulous intentions operators might have to begin with. Or, they may simply be unwilling to formally engage in such responsibilities in the absence of a paid service contract.

This article’s objectives therefore are:
- Firstly, presenting the utility of PDF as a useful format for distributing documents to a wide audience, without having to concern oneself with what software individual audience members may or may not have access to, if at all, and regardless of reason(s);
- Secondly, presenting safe, free software and open-source software options for using and editing of PDF files;
- Thirdly, beyond the general promotion of free and open-source software and PDF editing, this article is not about promoting nor deriding particular OSes or software packages, or strictly speaking their strengths or weaknesses.
As such, if a particular system or software package suits your needs and / or purposes, you should use it.
However, if a given preferred solution is costly software, perhaps your organization (or your family) may find it to be financially worthwhile to only purchase a minimum number of licences and only install it on a minimum number of designated computers, instead of needlessly on every computer in your organization (or family).
A simple cost / benefit analysis would be worthwhile: You should consider whether you wish to pay $5, $10, $15, or more, on a recurring basis (perhaps monthly), per computer on which such software would be installed. The costs, be they one-time costs or recurring, should be considered against how often the software may be used, perhaps in some cases only once or twice monthly — perhaps overall, let alone for each individual instance, depending on your organization’s size, needs, and other considerations. Further, it should be considered what operations are typically executed, especially if they simple operations such as joining multiple PDFs, or extracting a page or two, which can be easily performed by many, using any of a multitude of software packages you can get without cost, as opposed to perhaps more technical tasks which may justify costly specialized software.
Creating PDFs from an established document
To begin with, most software which create documents will have an option in the File menu or elsewhere to Print, or Print to Document, or an Export function, which will offer PDF as a format:
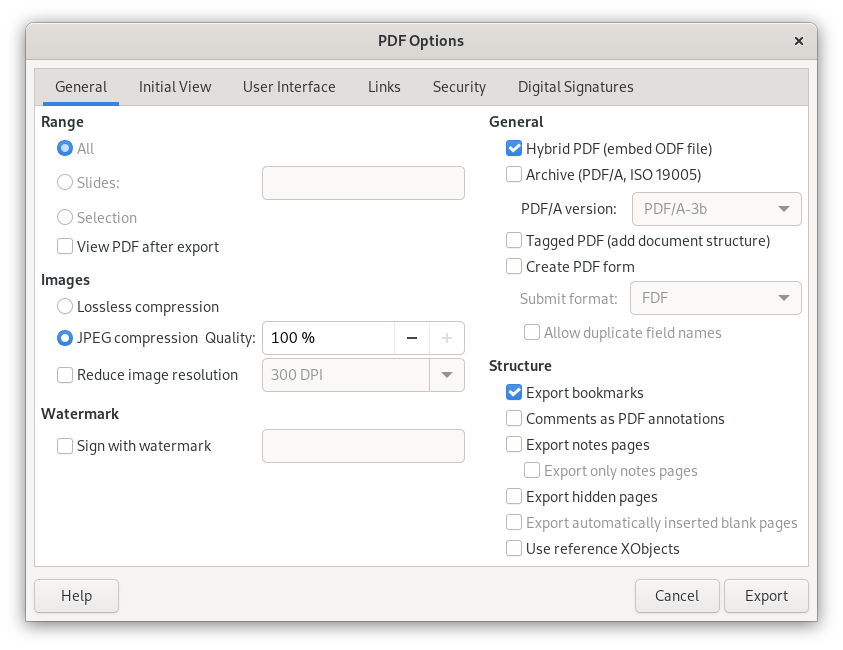
At the risk of skipping ahead to the PDF splitting section below, note that it is a common option to be able to selectively output some, instead of all, pages to the resulting PDF, thereby avoiding the question of having to later split the PDF to get only the desired page(s).
Overview of PDF Software
Perhaps (or perhaps not) to the surprise of many, there are many software packages and suites which will:
- Display PDF files
- Combine, divide, and export PDF files, as well as reorder pages within a PDF;
- Edit PDF files, such as the overall files and the file metadata, as well as the PDF file content
- Import and display PDF files according to particular strengths (The Gimp, Inkscape, e-readers)
Displaying PDF files:
Here are some examples of software which will display PDF files directly:
- Evince Document Viewer (Gnome Project)
- Okular (KDE Project)
- Firefox and Chromium (Web Browsers)
- PDFSam (limited free version; there is also a commercial version with more capabilities); a version for Debian derived Linux systems is available on their website
Here is a very short list of software which will open and display PDF files and allow editing, each according to their strengths, but whose primary function is not PDF display:
- LibreOffice (Office Suite)
- Calligra (Office Suite)
- The Gimp (Image Manipulation)
- Inkscape (Vector Graphics Editor)
Evince Document Viewer
Chromium (web browser)
Okular
Software to Combine PDF files
A relatively common activity is to combine multiple PDF files into one file — such as, separately scanned pieces of paper, or PDF files produced separately, perhaps by different people.
Here are some examples of software which will combine PDF files:
- PDF Mix Tool
- PDF Arranger
- PDF Mod
- PDF Jumbler
- PDFedit
- PDFTricks
- PDFSam
- LibreOffice
- Calligra Suite
- The Gimp
Combining PDF files in PDFArranger
Software to Divide PDF Files / Extract Pages
Another relatively common activity is to divide a PDF File, or extract one or more pages from a PDF file.
Note that if you are the creator of the document, as shown earlier, the software you used to create the document likely allows for you to selectively export individual or multiple pages to PDF in addition to exporting the entire document.
Here are some examples of software which will divide PDF files / extract pages:
- PDF Mix Tool
- PDF Mod
- PDF Jumbler
- PDFedit
- PDFTricks
- PDFSam
- LibreOffice — allows to print and / or export one or more pages
- Calligra Suite — allows to print and / or export one or more pages
- The Gimp — allows to print and / or export one or more pages
Splitting a PDF File with PDFMod
PDF Editing
Here are some examples of software which will edit PDF files to varying degrees:
- LibreOffice permits the possibility of creating a hybrid PDF and .odt / .ods file (word processor or spreadsheet files), which will allow for the PDF to be more easily edited by any suite that is able to edit .odt and .ods files; create a document with LibreOffice, and in creating a PDF, choose Export — General — PDF Hybrid (incorporating .odt / .ods file)
Other software to edit existing PDF files:
- LibreOffice Draw
- The Gimp
- Scribus
- PDFedit (old, but good)
- jPDF Tweak (old, but good)
- PDF Mix Tool (Basic functions)
- https://itsfoss.com/pdf-editors-linux/
- https://alternativeto.net/software/pdf24-creator/?platform=linux
- PDFFill (pdffill.com) (Windows)
In my personal experience, PDF editing — and ease of doing so — can vary wildly according to what one wishes to do, as well as wildly according to the nature of the source PDF. I have had excellent experiences editing a PDF created from a CAD software drawing (presumably created using commercial CAD software such as AutoCAD), and whose individual elements could be manipulated in LibreOffice Draw. I have also used LibreOffice Draw to insert text zones, arrows, and scanned signatures into PDFs. Conversely, documents composed primarily of scanned images — including text and forms — may require more image manipulation skills to edit, modify, and manipulate individual and specific elements of the document, depending on your objectives.
What you can do will also be dictated by which software package you choose and its strengths and weaknesses.
For instance, it should be noted that the phrase “Editing a PDF” can be a nebulous thing which can mean many and different things to many and different people. For instance, actually editing document text directly in the PDF may be what one understands and expects, while the strengths of a given piece of software may lay elsewhere.
LibreOffice has some PDF import functions, as well as imperfect document layout functions. Depending on the source PDF document, it can be quite effective at editing text directly.
Note from the closed-source world: I once had an excellent experience with a moderately-difficult-to-edit PDF using Microsoft Word, which included being able to edit the text — and presumably save in MS Word’s native file format.
Importing and editing a PDF in LibreOffice Draw (note the imperfect import):
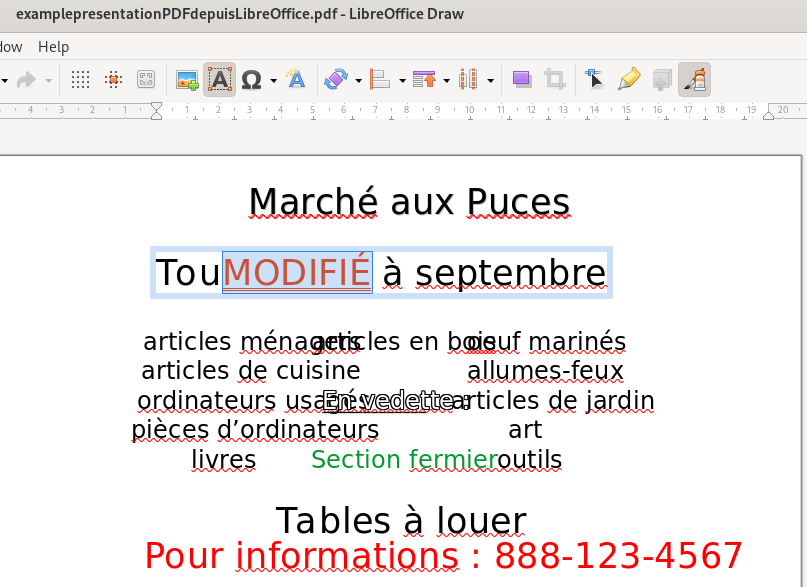
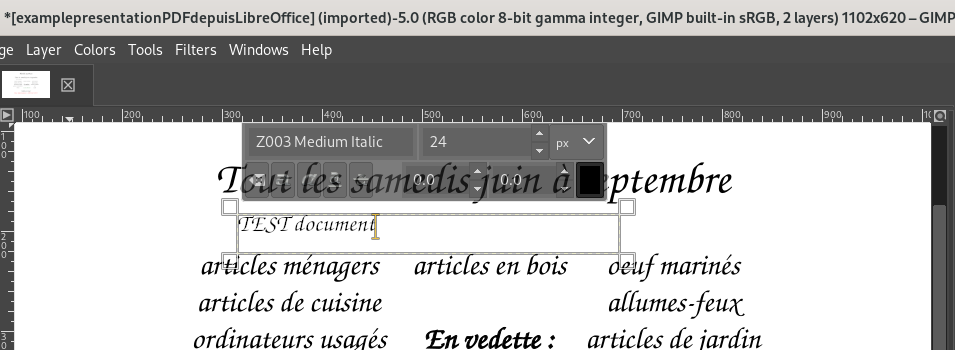
In the case of my example PDF, LibreOffice Draw allows for some direct editing of the text (Notice the word “MODIFIÉ” with a brick-red text colour replacing some of the text):
Importing and editing a PDF in Scribus, a desktop publishing programme:
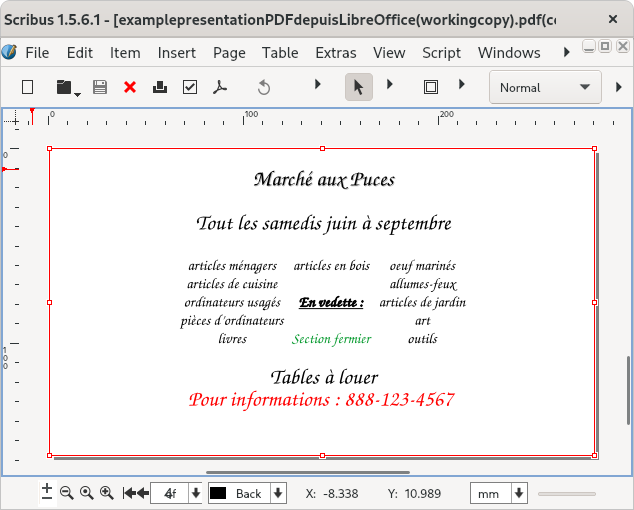
The Gimp can insert text zones into a PDF, and which text zones themselves may be edited within The Gimp; however, its strengths lie in dealing with a PDF as an image, and editing image characteristics, while editing the text as one might in a word processor might be more challenging.
Importing a PDF file into The Gimp, image manipulation software:
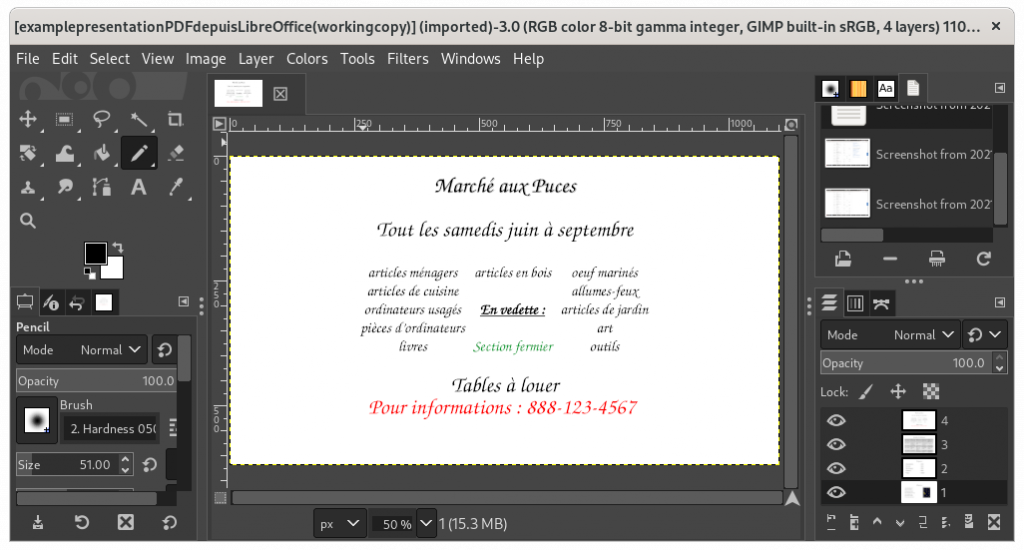
Adding a text zone to a PDF in The Gimp:
Exporting Text, Cut & Paste, and .odt File Creating
Depending on the source PDF and its nature, “cut & paste” may work (as opposed to not working at all), and may even “work well”, although this may be wildly variable according to the source PDF document. However, even in the best case, this method will normally only copy the actual text, and some of the images, from your PDF document; it may not usually be particularly useful in actually replicating the PDF document formatting.
As for other document and content formats, such as drawings, pictures, and text rendered into images, other sections of this post should be consulted (ie. using LibreOffice Draw or The Gimp for drawings; optical character reading (OCR), including OCRFeeder, etc.)
In addition to the mention of LibreOffice above, OCRFeeder is software that acts as a front end to optical character recognition software, and is able to import PDF files, and then export in HTML, plain text, OpenDocument (.odt) format, and of course PDF. Again depending on the source file, results may be variable, although the results are usable.
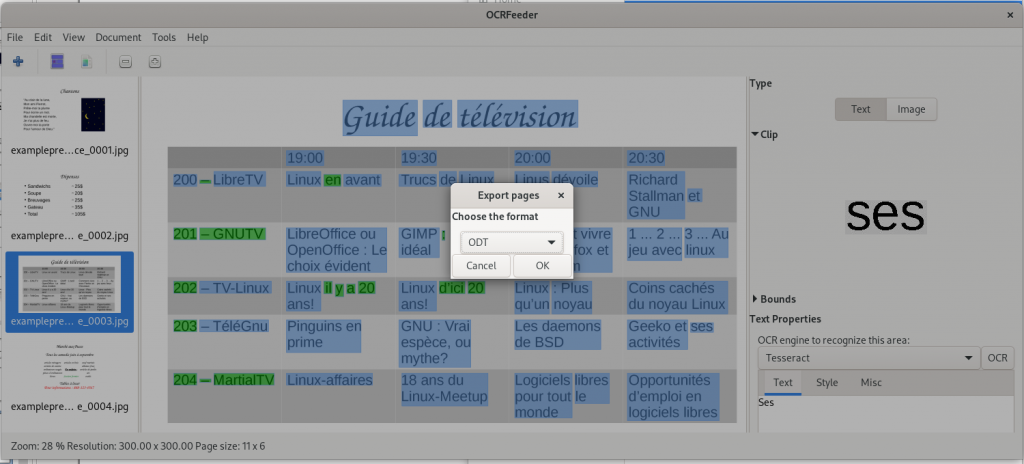
… and here is an image of the exported .odt file (word processor file) of the page viewed and created in OCRFeeder, then opened in my word processor (LibreOffice):
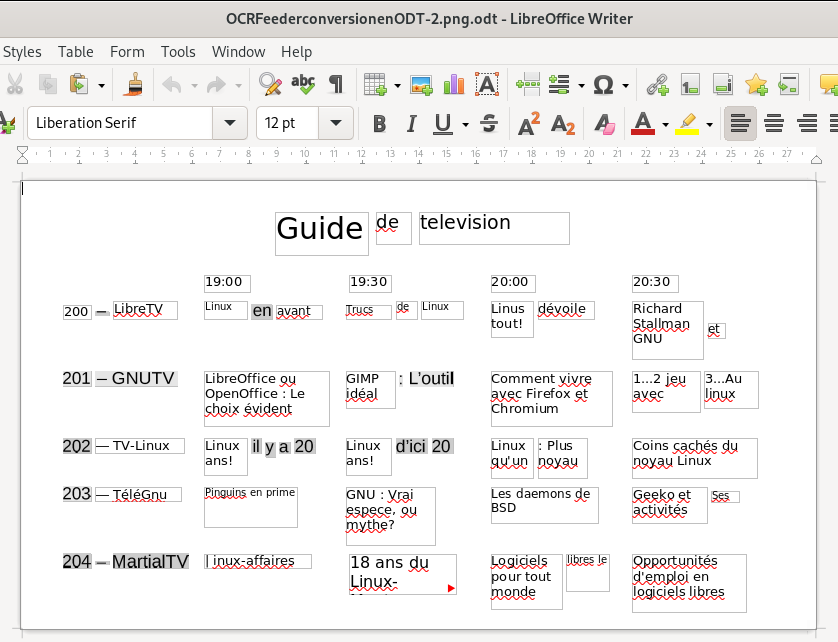
Ironically, as this case shows, the changes (or lack of adequate recognition and / or translation of the original layout) can be as great or even more as can occur by simply sharing documents between not-fully-compatible-though-similar software suites. However, though far from perfect, it is arguably usable, depending, of course, on how much effort you are willing to devote to replicating the original document layout — and then making your desired changes, and finally creating a new PDF document.
Exporting to other file formats:
As has been (indirectly) demonstrated several times throughout this post, PDF files can be imported into software that isn’t specifically dedicated to PDFs, and then allow for the resulting imported file to be exported into other formats. For example, The Gimp was used to create most of the working images for this post: In the case where PDF files were to be displayed, the PDF files were imported into The Gimp, and then exported in jpeg or png formats. This type of conversion — from PDF to another given format — can often be done by other pieces of software (to varying degrees) according to their strengths or weaknesses.
Photo Editing with PDFs
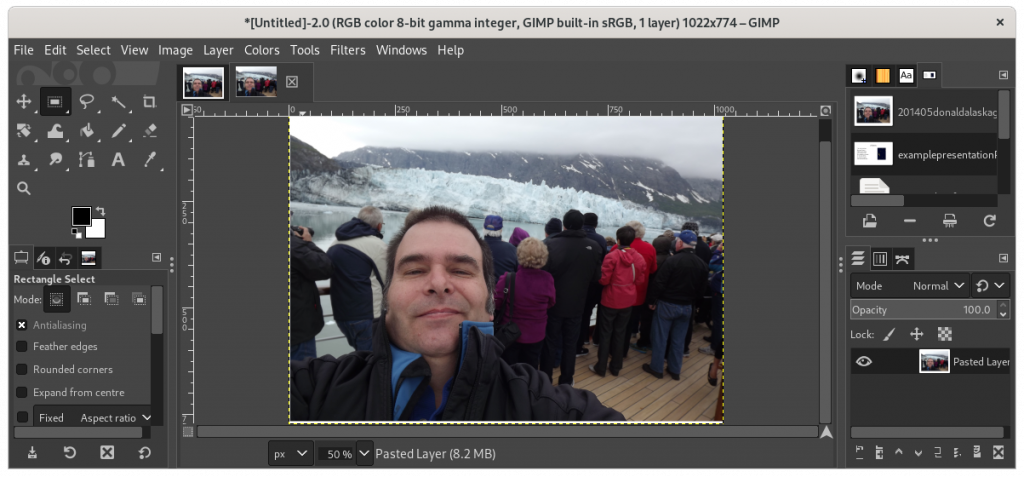
The Gimp is fully functional image processing software, very similar to — but, unfortunately, not fully compatible with nor a perfect drop-in replacement of — Photoshop. Using The Gimp, you can import a PDF and edit the image(s) directly, or extract photos and other images through a variety of means, such as selecting the area of the photo, copying the selected area, and creating a new document from the clipboard.
Here is a The Gimp having imported a PDF of a photo of myself on a cruise:
During the live presentation, I gave the hypothetical example — for the sake of levity — of a barber who particularly likes sideburns, and seeing mine in a PDF, decided to clip out one of my sideburns from the photo …
… and then notice on how I was starting to go grey at the time :
It is taken as an understood that use of The Gimp to manipulate the photo can be continued at this point — such as how my sideburns might look after a colouring, or to compare side-by-side against other people’s sideburns — and then the result exported as a PDF.
PDFTricks allows for resizing of images in PDFs, principally compressing and reducing the file size to the order of “large”, “medium”, “small”, and “extra-small”, as well as image exporting to .jpg / .png / .txt formats, and file merging and splitting.
During the presentation, the PDF document above composed of the photo of myself on a trip was run through the software’s “extreme compression” option. The following is a clip from a screenshot from a file manager, showing the size difference between the the original file, and the newly created compressed file:
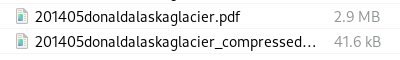
LibreOffice Draw allows for some image manipulation.
In this particular situation, the night sky drawing in the karaoke page of the example PDF I created was selected, and the various options directly available were shown. However, as mentioned earlier, I have imported PDF documents of building plans and modified them to include notes showing were works were performed, or to add signatures to documents.
PDF Forms
PDF Form Creation
LibreOffice Writer and Calligra Suite are fully-featured for the creation of forms. Unfortunately, I am not particularly adept at creating forms.
Filling PDF Forms
- Evince — if the PDF form was designed to be interactively filled
- Okular — if the PDF form was designed to be interactively filled
- The Gimp — allows for text areas to be inserted, as well as photos, drawings, and the like
- LibreOffice Draw — allows for text areas to be inserted, as well as photos, drawings, and the like
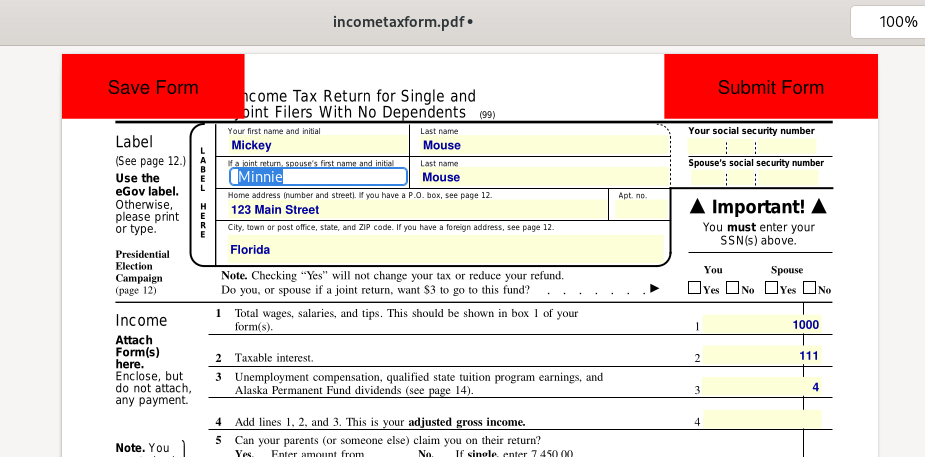
Here is an example form found at https://www.aloaha.com/sample-fillable-pdf-forms/ — a sample tax form which I began filling out for Mickey and Minnie Mouse, using Evince:
Final Choices:
- Viewing / displaying PDF files : User’s choice (usually a system’s default PDF viewer is adequate, or a web browser)
- Combining and splitting PDF files : PDFMixTool
- Editing PDF files : User’s choice (depends on objectives and source file; The Gimp and LibreOffice Draw are good contenders)
- Adjusting PDF file size : PDFTricks
- Form creation : User’s choice
- Form filling : User’s choice (usually a system’s default PDF viewer is adequate, or a web browser)
- Exporting PDF to other formats : OCRFeeder (for .odt); LibreOffice Draw (Photos and images); The Gimp (photos and images)
Note on Linux availability of the above software:
Here are some screen shots from my system’s installed repositories (Fedora Stable; Fedora Updates; rpmfusion.org — free and non-free)
PDF software easily accessible from my computer’s software repositories (“App Stores”):
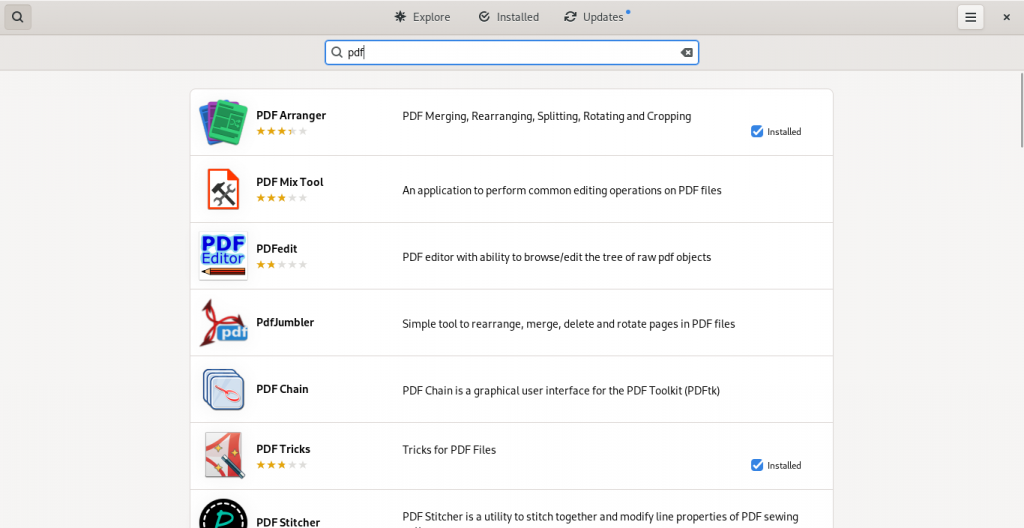
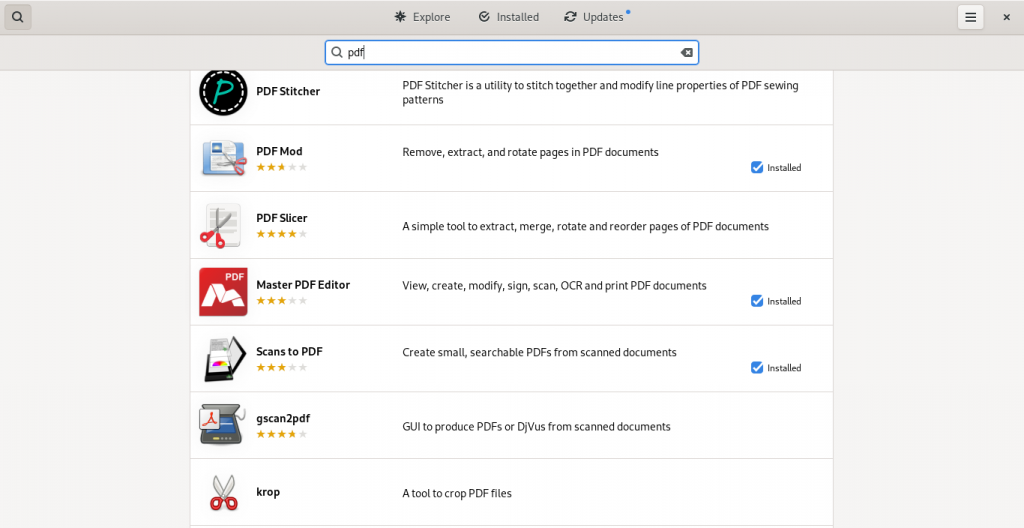
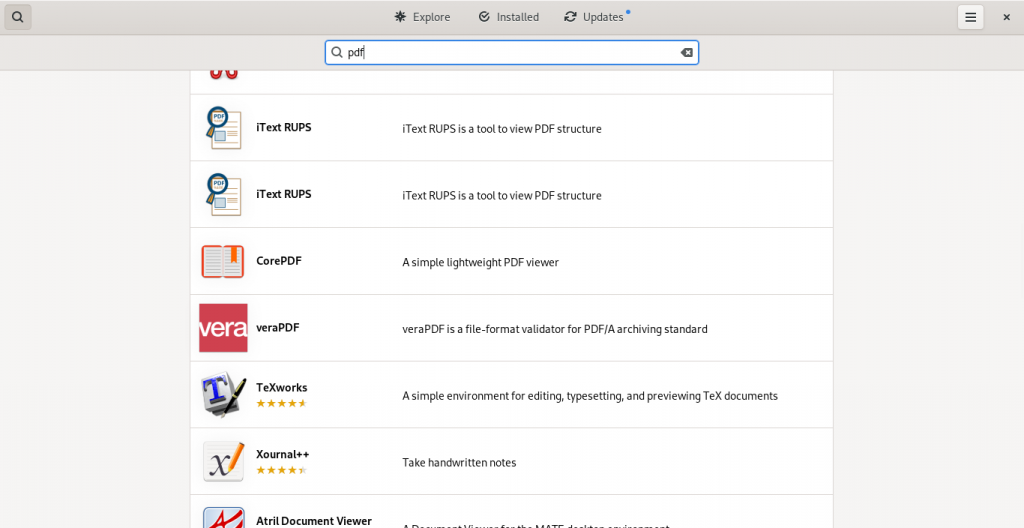
As this list suggests, there is lot of software available which have varying PDF abilities, ranging from being dedicated PDF software of various kinds, to other pieces of software with other principal functions but with PDF functions ranging to simple importing from and exporting to the format, to being useful within the limits of the software’s main functions to manipulate PDF files in some way(s).
Summary:
This presentation’s goals are to highlight:
- how PDF files are well supported most of the time on most systems, while the various pieces of software, between two versions, typically a well-known closed source project and an open-source counterpart, for document production, are not as compatible with each other as we may want;
- free software while avoiding the security risks inherent to using unknown and potentially dangerous websites, as well as software which is easily available for routine tasks as well as to reduce costs;
- the possibility of editing PDF files with various pieces of free software which are easily available in most Linux distributions’ repositories — as well as often easily available for other platforms — albeit occasionally with variable success.
Questions taken during the presentation:
A question asked midway through the presentation expressed a certain surprise that The Gimp can be used to edit PDFs. As mentioned earlier, The Gimp is able to import PDF files, and perform various functions on the file according to its strengths (image manipulation).
A participant asked at the end during a question period about a recommendation for software to affix signatures to documents. I replied that I was not aware of any open source official signing software with digital traceability, simply because that I had not done any research on that subject; however, an image of a scanned signature can usually be inserted in a document using The Gimp or LibreOffice Draw, or as a document is being created in a word processor.
A final comment recommended the use of LibreOffice Draw, based on the commentor’s frequent use of it to perform a number of the functions listed here, to which I’d commented that I had asked my employer’s IT department to install LibreOffice on my work-issued Windows-based laptop computer in order to be able to perform some drawing-modification functions as part of my employment.
Enjoy sharing and editing PDF files!
UPDATE 20220407:
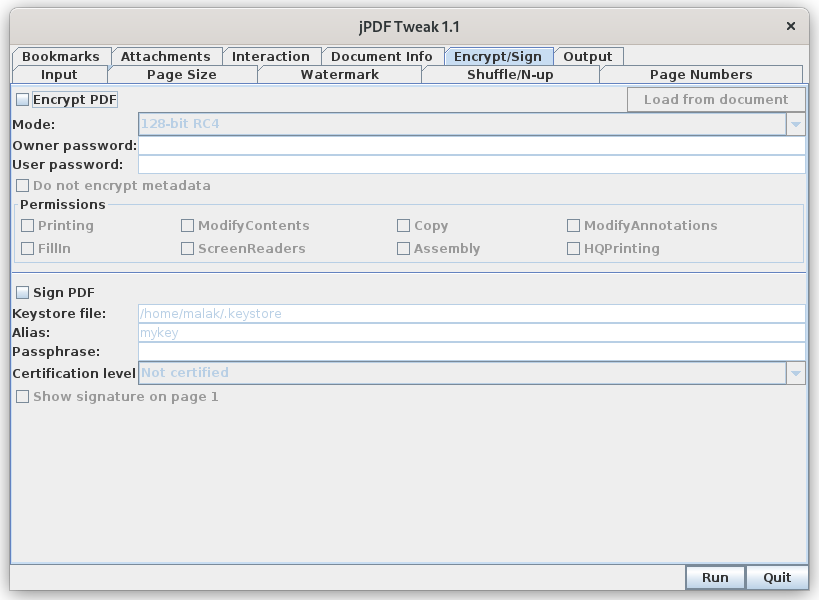
Signing PDFs can be performed with jPDF Tweak.
JPDF Tweak can also encrypt and add passwords to a PDF.